What Is Solar Wind?
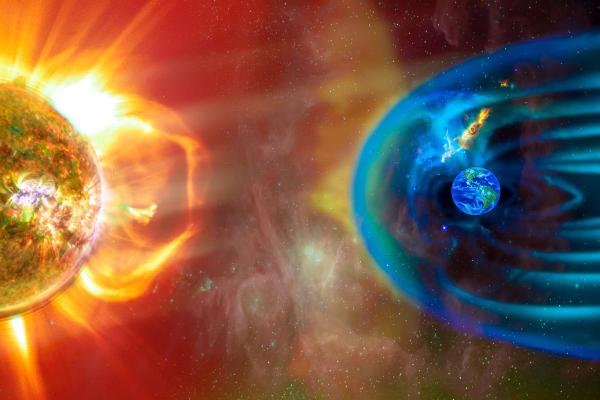

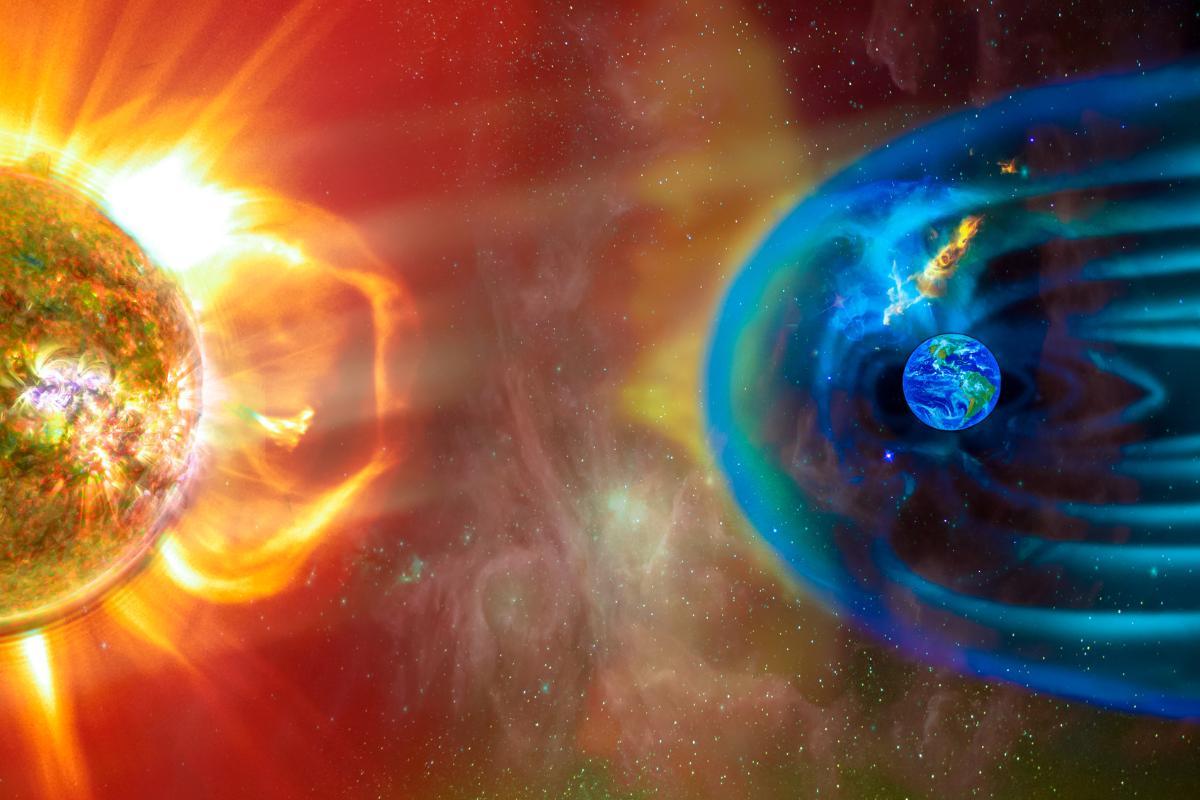
Solar wind shapes our space environment in many different ways. This continuous stream of charged particles flowing from the Sun's outer atmosphere travels millions of miles through space before encountering Earth's magnetic shield. While much of this cosmic wind goes unnoticed in our daily lives, its effects ripple through our atmosphere, influence our technology, and create some of nature's most spectacular displays.
In the following article by thedailyECO, we explore solar wind and its various impacts on Earth, examining how this phenomenon affects both our atmosphere and our daily lives.
What is solar wind?
Solar wind is a continuous stream of charged particles (primarily protons and electrons) that flows outward from the Sun's atmosphere into space.
The process begins in the Sun's corona, which is its outermost layer of atmosphere. Here, temperatures reach over a million degrees Celsius, making the plasma so hot and energetic that the Sun's gravity can't hold it back. As a result, the particles achieve "escape velocity" and stream outward into space.
The Sun's magnetic field plays a crucial role in this process. The field lines start out closed near the Sun's surface, but as the particles push outward, they stretch and eventually break these magnetic field lines. This process, called magnetic reconnection, helps accelerate the particles. The magnetic field also shapes how the solar wind flows through space, creating complex patterns as the Sun rotates.
Solar wind comes in two main varieties:
- Fast solar wind: which travels at about 800 kilometers per second, originates from "coronal holes" - regions where the Sun's magnetic field lines are open, allowing particles to escape more easily.
- Slow solar wind: moves at roughly 400 kilometers per second and typically comes from regions near the Sun's equator and areas with more complex magnetic field structures.
These solar winds have a significant impact on the dynamics of our solar system. They can erode planetary atmospheres, energize particles to create stunning auroral displays, and induce geomagnetic storms that can disrupt satellite communications and power grids. The following sections will examine these effects in greater depth.
Did you know the Sun has multiple layers, each playing a unique role in creating solar wind? Explore the anatomy of our star in our other article.
How solar wind affects Earth
Solar wind might be invisible to our eyes, but its effects on Earth are both profound and far-reaching. When this stream of charged particles from the Sun encounters our planet, it triggers a chain of interactions that affect everything from our atmosphere to our technology.
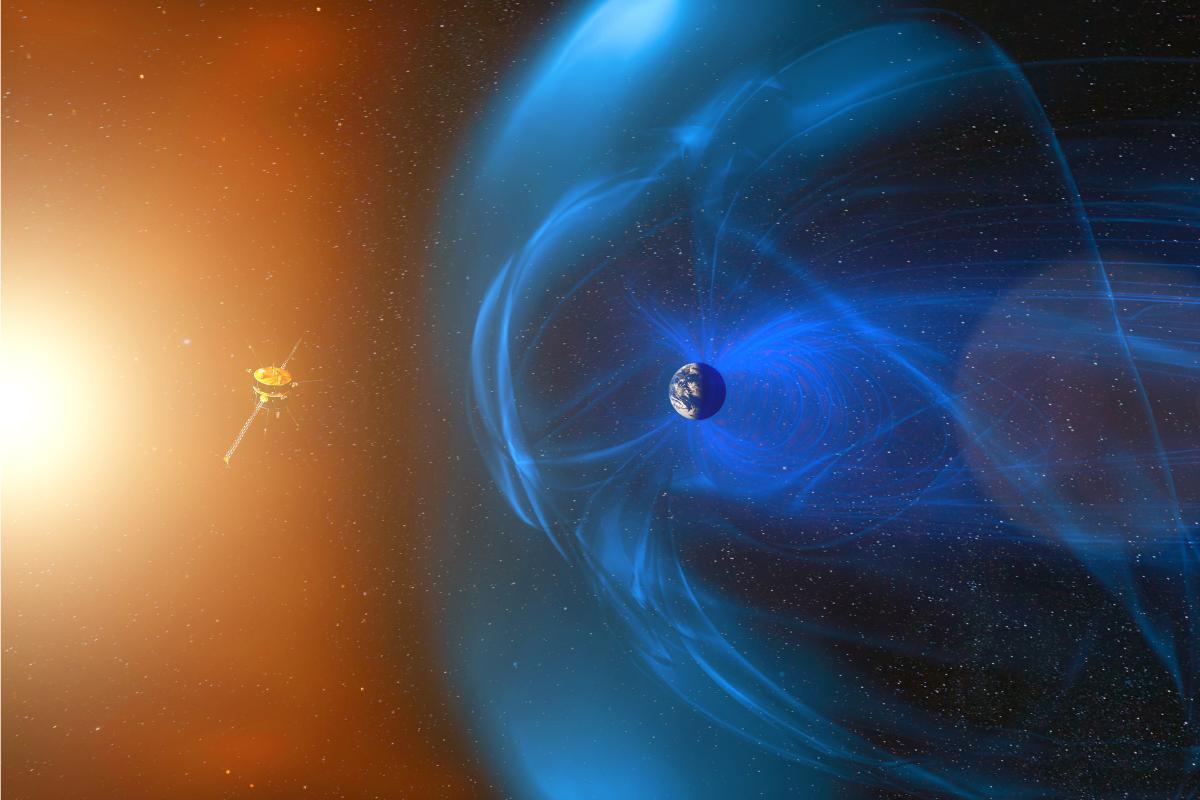
Our planet's magnetic field forms a protective bubble called the magnetosphere, which acts as our first shield against solar wind. When solar wind particles collide with this magnetic shield, they create a specific shape, compressing the magnetosphere on the Sun-facing side and stretching it into a long "tail" on the night side, much like a comet's tail in space.
Solar wind's effects can also be disruptive. During intense solar wind events and solar storms, these charged particles can wreak havoc on multiple technological systems simultaneously. The effects begin in space, where they interfere with satellite signals and can potentially damage satellite electronics. On Earth, GPS systems suffer from degraded accuracy or experience temporary failures. More seriously, these solar events can induce electrical currents that overload power transformers, triggering widespread blackouts. They also disrupt high-frequency radio transmissions, sometimes blocking them entirely. These effects on our interconnected technologies expose our fragility to the Sun's immense power, even from millions of miles away.
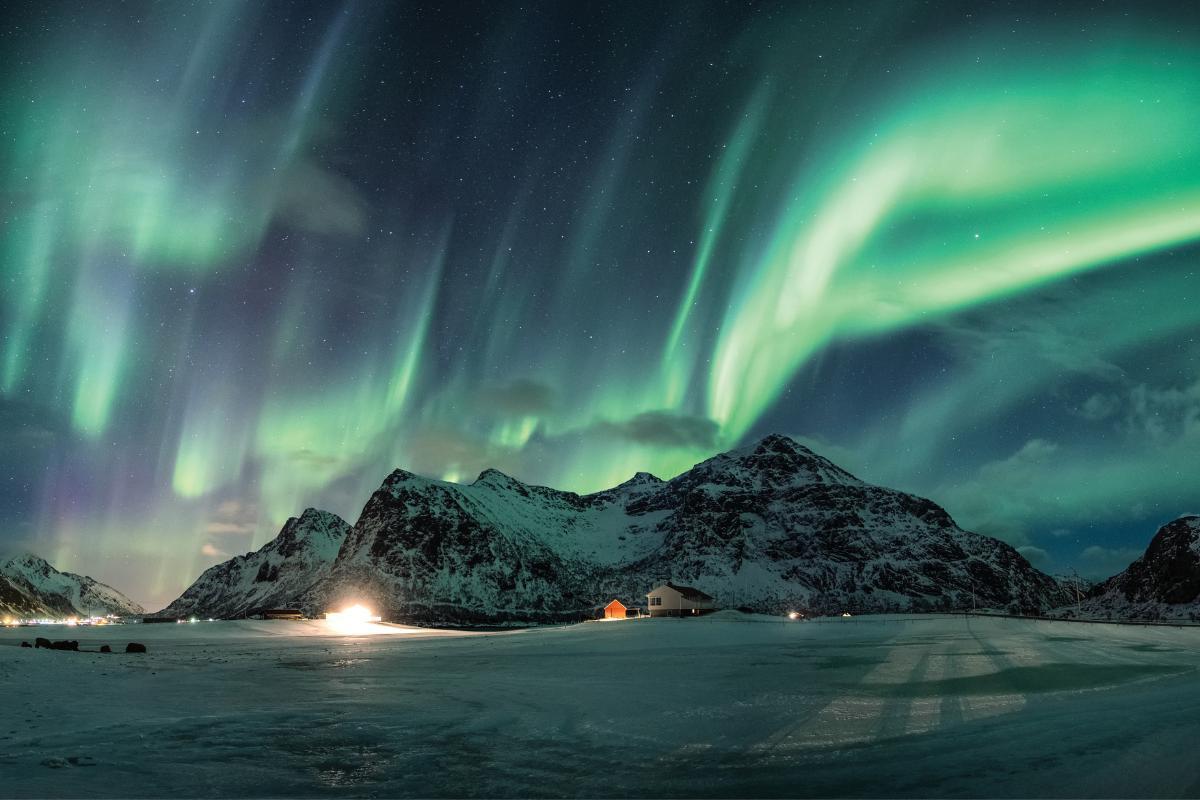
How solar wind causes auroras
One of the most visible effects of solar wind is the creation of auroras, both the Northern Lights (Aurora Borealis) and Southern Lights (Aurora Australis). These ethereal displays occur when solar wind particles manage to penetrate the upper layers of our magnetosphere and interact with atmospheric gases. When these charged particles collide with oxygen and nitrogen in our atmosphere, they create the famously known curtains of colored light we see near Earth's poles. Learn more about this dazzling phenomenon in our other article.
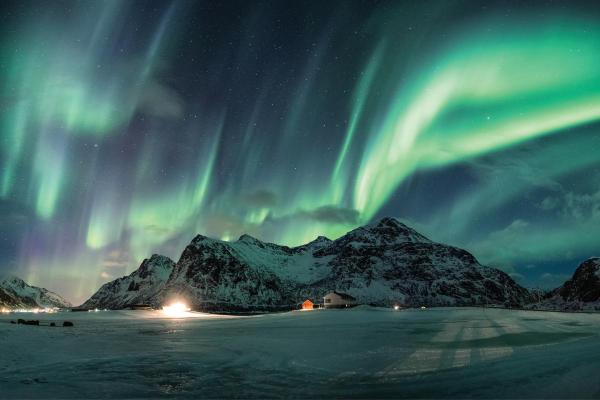

How solar wind affects Earth's atmosphere
Solar wind also shapes Earth's atmosphere through multiple processes, creating a chain of effects that reaches from the edge of space to the layers above our heads.
In the thermosphere and exosphere, solar wind particles collide with gases, changing their temperature and movement. These collisions lead to a significant process: they control how fast gases like hydrogen and helium escape into space.
Beyond this initial impact, solar wind transforms the chemistry of the upper atmosphere. When particles enter these layers, they break molecules apart and create ions, triggering reactions that alter the ionosphere's composition and electrical properties. This chemical transformation plays a key role in how our upper atmosphere behaves and interacts with space weather.
As solar wind heats the atmosphere, it expands and changes density at different heights. These density shifts create a ripple effect in space operations. Satellites must adjust their paths to maintain their orbits, while space debris moves unpredictably. This movement poses an ongoing challenge for space traffic management and satellite operations.
Curious about Earth's natural shield against solar wind? Discover how our planet's magnetic bubble protects us from space weather.

Are solar storm and solar wind the same?
Solar wind is a constant phenomenon because, as mentioned before, it refers to the continuous stream of charged particles that flows outward from the Sun's corona into space. It is always present but varies in speed and density. This steady flow occurs during both quiet and active solar periods.
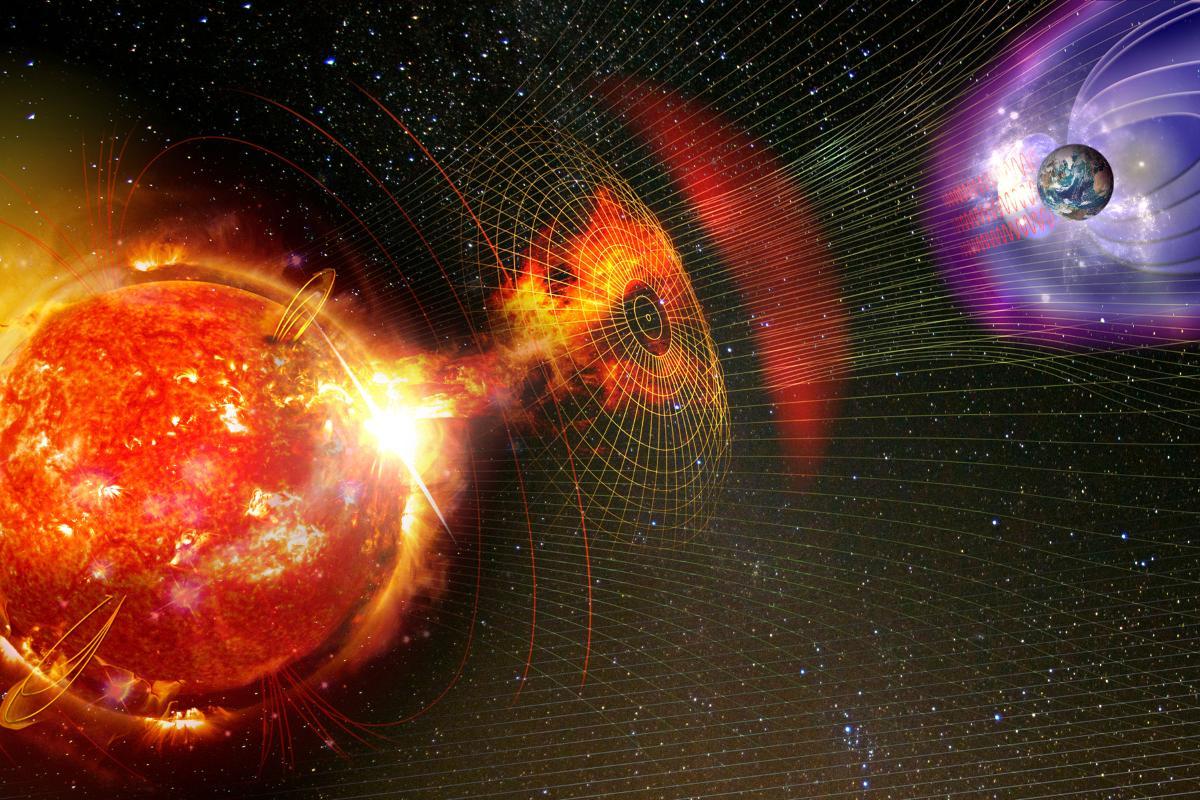
Solar storms, on the other hand, are intense eruptions or disturbances that occur on top of this baseline solar wind. Solar storms actually come in several forms:
- Solar flares: are powerful bursts of radiation that erupt from the Sun's surface, releasing X-rays, ultraviolet radiation, and radio waves. These travel at light speed, reaching Earth in 8 minutes, and can immediately affect our planet's upper atmosphere and radio communications.
- Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs): are large expulsions of magnetized plasma from the Sun's outer atmosphere. While often associated with solar flares, they're distinct events that release billions of tons of solar material into space. CMEs move more slowly than flares, typically taking 1-3 days to travel from the Sun to Earth.
- Solar proton events: occur when the Sun releases streams of highly energetic protons into space. These particles travel faster than CMEs but slower than flare radiation, usually reaching Earth in several hours. These events pose significant radiation hazards to satellites, spacecraft, and particularly to astronauts working in space.
When these solar phenomena reach Earth, they can trigger geomagnetic storms, which can cause significant disturbances in Earth's magnetic field and upper atmosphere. The intensity of these storms depends on the strength of the incoming solar phenomena and how their magnetic fields interact with Earth's own magnetic field.

Do solar winds cause geomagnetic storms?
Solar wind alone doesn't typically cause geomagnetic storms. As mentioned before, only enhanced or disturbed solar wind conditions can trigger them. The regular, steady solar wind that flows past Earth usually just causes mild compression of our magnetosphere without creating a storm.
The key factor in creating a geomagnetic storm isn't just the presence of solar wind, but rather its strength, speed, and magnetic properties. When these properties become extreme, the magnetic field it carries may point strongly southward. This southward-pointing field can connect with Earth's magnetic field. Once connected, it transfers large amounts of energy to our planet's magnetic system. This energy transfer is what triggers a geomagnetic storm.
Can geomagnetic storms hurt humans?
Geomagnetic storms generally don't pose direct health risks to humans on Earth because we're protected by our atmosphere and magnetic field. However, the situation changes for people at high altitudes airline crews and passengers on polar routes may face increased radiation exposure during strong storms, while astronauts in space face even greater risks and may need to seek shelter in protected areas of their spacecraft.
The main concerns for most people come from indirect effects when these storms disrupt our technology and infrastructure. If a powerful storm causes widespread power outages, it could affect critical services like hospital equipment, water systems, and food storage. Similarly, when storms interfere with communications and navigation systems, they can disrupt emergency services, air traffic control, and crucial safety alerts.
Beyond solar wind, Earth's atmosphere crackles with electrical activity. Explore these fascinating phenomena in our other article.
If you want to read similar articles to What Is Solar Wind?, we recommend you visit our Facts about Earth and the universe category.