What Is Biomass Energy?


In the quest for sustainable and renewable energy sources, biomass energy seems to be a versatile and promising option. Derived from organic materials like plants, agricultural residues, and waste, biomass energy offers the potential to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change. However, like any energy source, biomass comes with its own set of advantages and challenges.
This article by thedailyECO explores what biomass energy is, along with its advantages and disadvantages.
What is biomass energy?
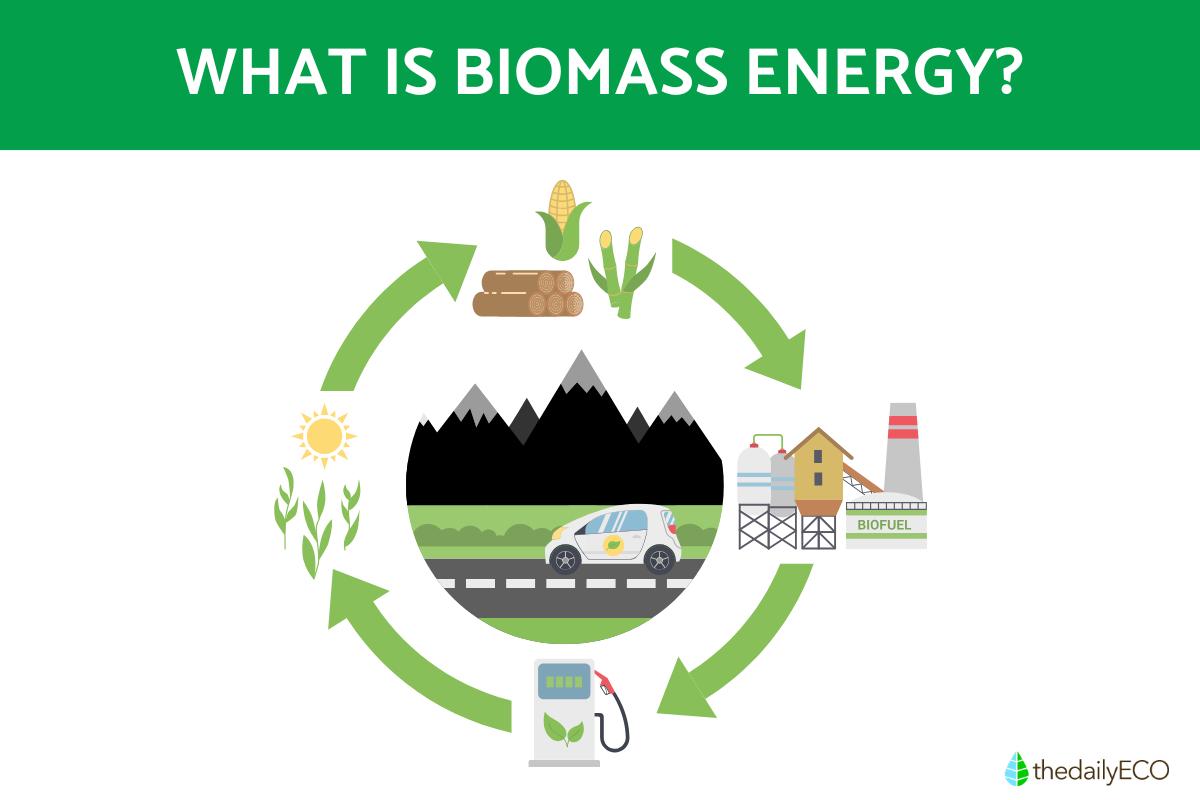
Biomass energy is energy derived from organic matter, plant and animal material that comes from recently living organisms. This organic matter can be processed through natural, industrial, biological, or mechanical means to produce energy. Because it comes from organic materials that can be replenished, biomass is considered a renewable energy source.
Types of biomass energy
- Natural biomass refers to organic material produced in natural ecosystems without human intervention. This includes dead trees, fallen leaves, and other plant materials that naturally accumulate in forests or other ecosystems.
- Residual biomass refers to organic waste generated by human activities. Examples include urban solid waste such as food scraps, forestry residues like branches and sawdust, agricultural residues and industrial organic waste like pulp and paper waste.
- Biomass produced involves dedicated crop fields where specific species are planted specifically for energy production. This includes energy crops like switchgrass, willow, and miscanthus, which are cultivated solely for their ability to produce biomass energy.
- Landfills generate methane gas as organic waste decomposes. This landfill gas can be captured and used to generate electricity or heat buildings.
While considered renewable, the sustainability of biomass energy depends on managing resources responsibly. Ensuring the source material is replenished and minimizing environmental impact during production are crucial for responsible biomass energy use.
How is biomass produced?
Biomass energy harnesses the chemical energy stored in organic matter and converts it into usable forms of energy. The process involves several methods, each leveraging different technologies to achieve energy conversion. Let us take a closer look at the most commonly used processes:
Direct combustion
This is the simplest and most common method. Biomass, like wood chips or pellets, is burned in a furnace or boiler. The heat generated boils water, creating steam that spins turbines to produce electricity. The leftover ash can sometimes be used as fertilizer.
This method utilizes well-established technologies like boilers, turbines, and generators, similar to those found in coal-fired power plants.
Anaerobic digestion
Anaerobic digestion is a biological process where microorganisms break down organic matter, such as manure, sewage, or food waste, in the absence of oxygen. The material is placed in an oxygen-free tank, where bacteria break it down, releasing methane gas or biogas. This biogas can then be burned directly to generate electricity and heat or upgraded to biomethane, which is a cleaner-burning alternative to natural gas.
This process also produces digestate, which is a nutrient-rich residue that can be used as a fertilizer.
Anaerobic digesters are large, sealed tanks equipped with temperature control systems to maintain optimal conditions for the bacteria.
Fermentation
This process uses microorganisms, like yeast, to convert sugars found in crops like corn or sugarcane into ethanol. The ethanol produced can be blended with gasoline to create biofuel for transportation. This bioethanol can be used in internal combustion engines.
Fermentation utilizes fermentation tanks where the biomass feedstock is mixed with water and yeast. The process requires careful control of temperature and pressure. The resulting ethanol needs to be distilled and purified before use through specific distillation units.
Advantages of biomass energy
This renewable resource offers a promising alternative to traditional fossil fuels, boasting potential for environmental friendliness and economic viability. Let us take a look at some of its most important advantages:
- It is renewable: unlike fossil fuels, which take millions of years to form, biomass is derived from organic materials that can be replenished through responsible cultivation and management practices. Planting new trees or crops to replace those used for energy ensures a continuous source of fuel.
- It is sustainable: biomass production can be integrated with sustainable forestry and agricultural practices. Techniques like planting fast-growing trees or using crop residues can minimize environmental impact while providing a steady supply of biomass.
- It is carbon-neutral: we know that plants absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere during photosynthesis. When biomass is burned for energy, the CO2 released is roughly equal to the amount absorbed by the plants during their growth. This creates a closed-loop system, making biomass energy potentially carbon-neutral, especially when compared to fossil fuels which release large amounts of previously stored carbon.
- It produces low emissions: while some CO2 emissions do occur during biomass production and processing, they are generally much lower compared to burning fossil fuels. Additionally, by diverting organic waste from landfills, biomass energy reduces methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas.
- It reduces waste: food scraps, yard waste, animal manure, and even leftover wood from construction can all be converted into usable energy. This not only reduces the burden on landfills but also creates a valuable resource.
- It diversifies the energy mix: biomass contributes to energy security by diversifying the energy mix, reducing reliance on a single source like fossil fuels. This diversification can lessen the impact of price fluctuations and geopolitical instability in major oil-producing regions.
- It is produced locally: many forms of biomass can be grown or sourced locally. This reduces dependence on imported fuels and promotes local energy independence, potentially creating more stable energy supplies.
- It creates jobs: the development and use of biomass energy can create new jobs across the supply chain, from forestry and agriculture to processing facilities and power plants. This can revitalize rural economies and provide opportunities for skilled workers.
- It is affordable: biomass is widely available across the globe and can be more cost-effective than some other forms of energy, especially in regions with abundant biomass resources.
If you are interested in learning more about what biomethane is, its advantages and uses, be sure to read this other article.

Disadvantages of biomass energy
While biomass offers exciting possibilities, it's important to acknowledge some potential drawbacks:
- It leads to deforestation and habitat loss: large-scale production of biomass crops can lead to deforestation, especially if unsustainable practices are used. This can disrupt ecosystems, endanger wildlife, and reduce biodiversity.
- It impacts the soil and water: intensive farming of biomass crops can deplete soil nutrients and require significant water resources. This can lead to soil erosion and stress on water supplies, impacting surrounding ecosystems.
- It has a large carbon print: compared to solar or wind power, biomass energy generally has a larger carbon footprint due to emissions from processing, transportation, and potential land-use changes.
- It is less efficient: converting biomass into usable energy can be less efficient than other renewable sources like solar or wind. Additionally, harvesting, transporting, and storing biomass can be expensive, impacting the overall economic viability.
- It can be expensive: developing and maintaining biomass infrastructure, like power plants and conversion facilities, can require significant upfront investments, potentially hindering widespread adoption.
- It can cause conflict: biomass production competes for land with food crops and natural habitats. This can lead to rising food prices and impact food security, particularly in regions already facing food scarcity.
- It is still being developed: some biomass conversion technologies, like gasification, are still evolving and require further development for optimal efficiency and environmental performance.
Recognizing these challenges is paramount to developing and implementing sustainable practices. By doing so, we can maximize the benefits of biomass energy while minimizing its drawbacks.
If you are interested in learning more about the main characteristics of renewable and non-renewable energies, be sure to check this other article.

If you want to read similar articles to What Is Biomass Energy?, we recommend you visit our Renewable energies category.