What is a Leucoplast?


Leucoplasts are small rounded structures that belong to the plastid family. These are membrane-bound organelles which are found in certain cells, mainly plants and algae. The functions of leucoplasts include lipid synthesis, carbohydrate storage and starch production. There are three types to carry out these different functions, including amyloplasts, elaioplasts (or oleoplasts) and proteinoplasts. In this article from thedailyECO, you can learn more about the function and types of these plastids with our article asking what is a leucoplast?
What are leucoplasts?
Leucoplasts are small structures that are found in certain cells that receive sunlight. As they are not cells in themselves, they are considered organelles. Specifically, they belong to the plastid family of organelles which are characterized by their lack of color. Leucoplasts are often found in non-photosynthetic tissues such as roots, bulbs and seeds. Their presence is essential for the storage of substances that facilitate plant growth and nutrition.
Pigmented plastids play an active role in photosynthesis. Conversely, leucoplasts are colorless and do not contribute to light capture. This means the function of leucoplasts is focused on the storage of essential compounds, making them crucial components in the structure and composition of plants. The absence of pigments in leucoplasts makes them less visible compared to other parts of the plant, although their importance should not be underestimated.
The morphology of leucoplasts is variable. They are often smaller than their pigmented counterparts. Their shape can be described as amoeboid, allowing them to adapt to different cell types and tissues. Overall, leucoplasts represent an integral part of plant cellular architecture. They contribute to their internal organization and to the maintenance of plant health through their storage capacity.
Plastids are found in plants, algae and other eukaryotic organisms. This means they are not found in animals or prokaryotic organisms. Learn about the difference between plant and animal cells in our releated guide to cellular biology.

Function of leucoplasts
We have explained the basic function of leucoplasts in the cells of plants and other eukaryotic organisms. Find out the specific functions below:
- Lipid synthesis: leucoplasts are essential for the production of lipids, which are transported to various areas of the cell. This function is essential for the formation and maintenance of cell membranes, as well as for energy storage.
- Nutrient biosynthesis: although they do not act as primary storage organelles, leucoplasts are responsible for carrying out a variety of vital biosynthetic functions. They are instrumental in the production of fatty acids, such as palmitic acid, and for the synthesis of numerous amino acids. In addition, they contribute to the formation of compounds such as heme, a compound which is important in various metabolic processes.
- Carbohydrate storage: the main function of leucoplasts is to produce and store vital nutrients, such as starch, proteins and lipids. They use glucose to produce starch, which serves as a carbohydrate reserve in plants. This ensure the plant has an energy supply during critical periods such as prolonged heavy cloud cover.
- Starch production: leucoplasts can transform glucose into starch, acting as a form of energy reserve. This starch is used at different stages of plant development, providing energy resources when conditions are unfavorable for photosynthesis.
- Diversity of metabolic functions: leucoplasts are not only limited to storage. They are also involved in the synthesis of essential compounds that support plant growth and development. This includes the aforementioned production of amino acids which are fundamental building blocks for proteins. They are also influential in producing other metabolites necessary for various biological functions.
Discover more about various metabolic processes in which leucoplasts are essential with our article explainging the difference between anabolism and catabolism.
Types of leucoplasts
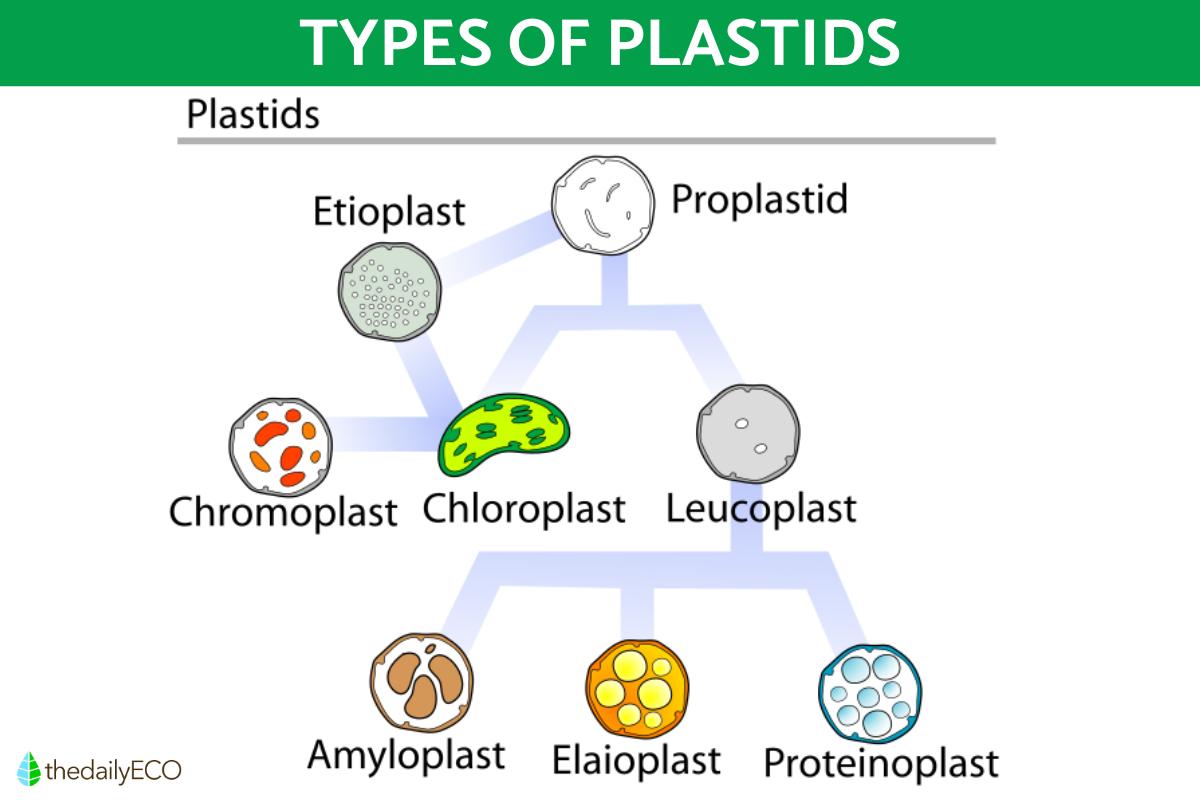
Leucoplasts are classified into three main types according to the substance they store These are amyloplasts, elaioplasts (or oleoplasts) and proteinoplasts. We look at them in more detail below:
Amyloplasts
Amyloplasts are responsible for storing starch which is the main form of energy reserve in plants. These structures convert glucose into starch and store it in tubers, seeds, stems and fruits. Chloroplasts produce starch in small amounts, but amyloplasts can synthesize and store large amounts of starch for long periods. These periods can range from days to years.
This storage ability of amyloplasts is vital to the plant, especially during periods without sunlight. During this time, starch can be broken down to release energy and continue the plant's survival. Special amyloplasts known as stratoliths also have an important role in sensing gravity, helping to direct root growth downward.
Discover the importance of roots as we look at the different parts of plants and their functions.
Elaioplasts
Also known as oleoplasts, elaioplasts are specialized for the synthesis and storage of lipids and oils. These structures are smaller than amyloplasts and contain numerous fat droplets inside. They are commonly found in seeds and cotyledons in which they play an important role in the development of pollen grains.
Elaioplasts are involved in pollen maturation, releasing lipids that form a protective layer on the outer part of the grain. Lipid synthesis in elaioplasts takes place through a prokaryotic pathway, which is different from the eukaryotic pathway that occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum.
We explain more about the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells in our related guide.
Proteinoplasts
Also known as aleuroplasts, proteoplasts are responsible for storing proteins. However, their existence as a type dedicated to this purpose is not completely clear. They are found primarily in the seeds of cereals, where they store high concentrations of proteins in the form of crystals or amorphous material. The function of proteoplasts is essential in seed development, providing the nutrients necessary for early plant growth.
Now that you know what leucoplasts are, you may be interested in our article explaining what is the cell wall and its various functions?

If you want to read similar articles to What is a Leucoplast?, we recommend you visit our Biology category.
- Pérez, F. (2017). Introduction to Plant Physiology. Plant Structure and Function: Cells, Tissues and Organs. Water Relations: Absorption, Transport and Water Loss. Transport of Organic Substances. National University of Ucayali.
https://biblioteca.unu.edu.pe/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/LIBRO-P1.pdf - Alvarado, S. (1918). Plastosomes and Leucoplasts in Some Phanerogams. Works of the National Museum of Natural Sciences.
https://bibdigital.rjb.csic.es/medias/78/e0/d6/73/78e0d673-393c-4dba-b3ce-0ccc6e47ae9b/files/P_0074_C_2.pdf