What Is a Circular Economy Business Model?


The circular economy is a business model which seeks to modify the dominant systems of resource production and consumption in a way which minimizes waste by re-entering materials into said systems for as long as possible. Not all materials can be reused, repaired or recycled, but those that can are put to use rather than simply becoming waste. The purpose of a circular economy is to minimiza waste and pollution as a means to combat climate change, ecosystem degradation and other detrimental environmental factors. We learn more about its benefits and examples as thedailyECO asks what is a circular economy business model?
What is a circular economy business model?
Our planet is facing many existential threats, greatly influenced by industry. The current rate and modes of production are leading to the depletion of natural resources and the destruction of ecosystems. Increases in population numbers, profligate consumption patterns and an excessive generation of waste place a massive strain on our limited resources. Industrial production also results in the deleterious effects of climate change.
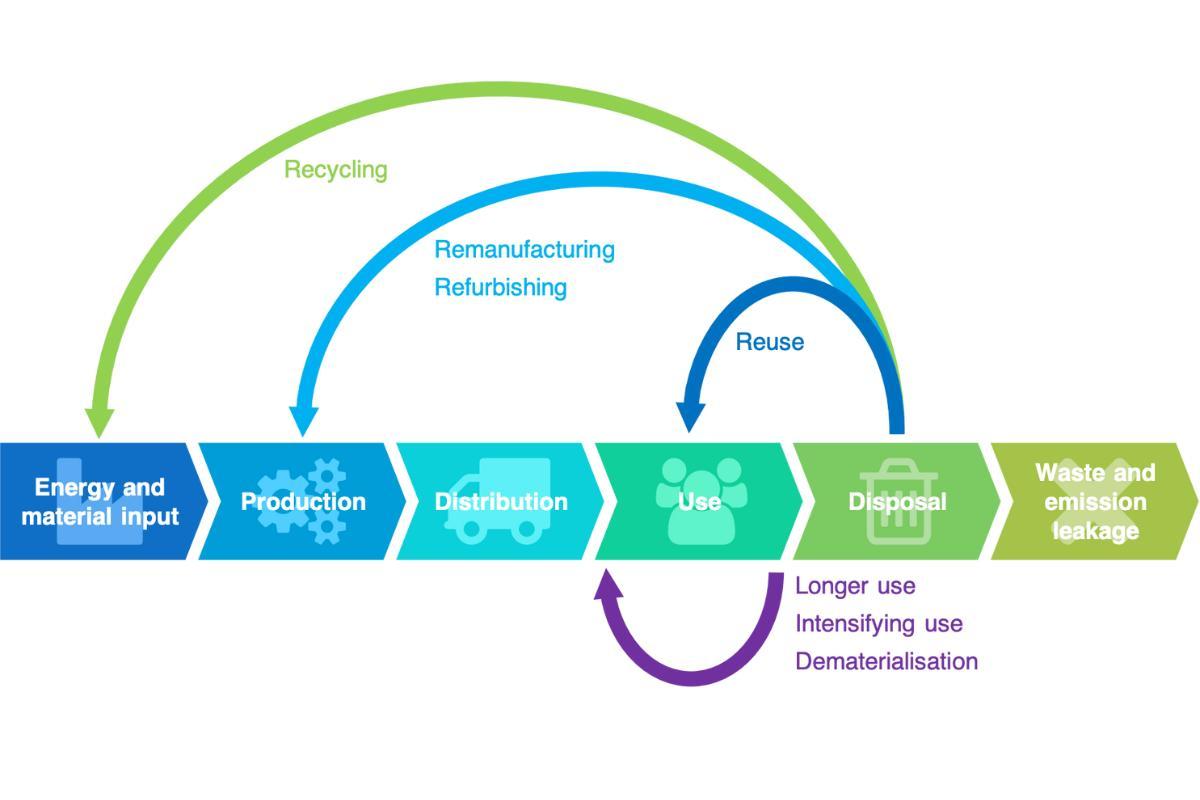
The concept of a circular economy business model is a result of such threats. It is a new business paradigm which seeks to modify the dominant models of production and consumption in a way which minimizes waste. This minimization is a result of reusing, repairing, refurbishing or recycling materials so they can be reentered into the production system.
Materials in a circular economy are preserved for as long as possible and their value is optimized. A circular economy is only possible if there is adequate waste management throughout the life cycle of a product. This requires better assessing resources and devising better methods of preservation.
It is important to view a circular economy as a type of business and production model. It is not an alternative to production and consumption, but an ecologically responsible approach to industrial capitalism. It does not necessarily offer environmental justice, nor does it address global economical inequality by definition.

Principles of a circular economy business model
The circular economy business model is based on the following three fundamental principles:
Preserve and enhance natural capital
This principle seeks to use natural resources efficiently, prioritizing renewable resources and reducing the consumption of non-renewable raw materials. The circular economy is not limited to just optimizing the use of existing resources, but also promotes the regeneration of ecosystems, promoting practices that aim to strengthen and restore natural capital.
Optimize the use of resources
This principle focuses on prolonging the useful life of products and their components through strategies such as reuse, repair, recondition and recycle. Ecodesign plays a key role, as it allows the development of products that are more durable, easy to disassemble and made from recoverable materials. This facilitates their reintegration into the production cycle with the least possible loss of value.
Improving system efficiency
For the circular economy to work effectively, it is necessary to optimize the performance of the system as a whole. This involves minimizing negative consequences, such as waste and polluting emissions. It also encourages the conversion of by-products from one industry into inputs for another. It seeks to make more efficient use of land, energy and natural resources, promoting synergies between the different actors involved in each process.
One industry which can see the application of circular economy practices is agriculture. Learn more with our article asking what is regenerative farming?
Benefits of the circular economy
With this circular approach to production and consumption, the benefits of this business model can be far reaching. They include the following:
- Waste reduction and environmental protection: promoting practices such as source separation, reuse and recycling allows materials to be reintegrated into the market. This can significantly reduce the amount of waste that ends up in its final disposal. This not only reduces the pressure on landfills and dumps, but also slows down the extraction of raw materials, minimizing the impact on ecosystems and biodiversity. By reducing waste generation and the use of new materials, greenhouse gas emissions are also reduced, helping to mitigate the effects of global climate change.
- Social inclusion: the circular economy promotes the integration of former informal waste pickers into the waste management system, giving them opportunities to formalize their work and improve their working conditions. This not only dignifies their work, but also allows them to access better income, social security and training, transforming waste recovery into a safer and more sustainable activity.
- It is a more energy-efficient process: recycling and reuse processes typically require less energy than the production of goods from primary resources. For example, the manufacture of recycled aluminum consumes up to 95% less energy compared to production from bauxite. Similarly, recycling plastic and glass can significantly reduce energy consumption in industry, decreasing demand for fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions in the process.
- It creates more resilient cities: the circular economy not only contributes to mitigating climate change, but also strengthens the adaptive capacity of our most vulnerable communities. By reducing the amount of waste before it reaches final disposal, various environmental and health risks that affect nearby populations are reduced. Reducing waste decreases the proliferation of vectors such as rodents and insects, which can transmit diseases. This shows how a circular economy can improve public health. In addition, it prevents the accumulation of volatile waste that can clog drains and stormwater systems, reducing the risk of flooding during periods of heavy rain.
Discover another method of improving sustainability in a city by reading our article on the benefits of urban forestry.

Examples of a circular economy business model
Resource management in production and consumption processes according to a circular economy is not yet widely implemented. However, we can see an increasing use of this approach in business models across various industries. Examples include:
- Production of biogas and compost from organic waste
- Circular fashion programs for reusing or recycling clothing
- Use of returnable packaging
- Recycling wood to create benches in public spaces
- Recycling of used tires to create new products
- Development of bioplastics from corn starch or fruit peels
- Use of recycled materials in construction
Reusing materials can be seen in using cement from building rubble or creating ecological bricks made from recycled plastics. Bioplastics can also be more compostable than traditional plastics, meaning they are less environmentally damaging even when they can no longer be reused or recycled.
Now you know the meaning of a circular economy business model, you may want to learn more about how sustainability practices can be applied to specific areas with our articles on what is the blue economy and what is a green city?
If you want to read similar articles to What Is a Circular Economy Business Model?, we recommend you visit our Environmental education category.
- De Miguel, C., Martínez, K., Pereira, M., & Kohout, M. (2021). Circular economy in Latin America and the Caribbean: opportunity for a transformative recovery. Project Documents (LC/TS.2021/120), Santiago, Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC).