What Are Tubers in Plants?


Tubers are unique structures present in various types of plant which are able to store water and nutrients. These nutrients are necessary for the growth of the plant, but they are also the reason they have become very important foodstuffs for humans. They are known to be very nutritious, although different types of tubers have varying nutrient profiles. While tubers are not technically a type of plant in themselves, many people refer to the plants which have the tuber structure as tubers. The enlarged tuber structure can be either part of the stem or part of the root, but they both grow underneath the soil.
At thedailyECO, we learn more by asking what are tubers in plants? We also provide 18 different types of tubers, as well as explain the difference between tubers and bulbs.
- What are tubers in plants?
- Types of tubers
- Tuber vs. bulb differences
- Examples of plant tubers
- Sweet potato
- Chufa
- Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus)
- Mashua
- Potato
- Yam
- Taro
- Yucca
- Water chestnut
What are tubers in plants?
In botany, the tuber is the part of a root or underground stem which is a specialized structure for the storage of nutrient reserves. Since they act as storage structures, they are enlarged in size, even if the plant above the soil is relatively small. The two main types of tubers are:
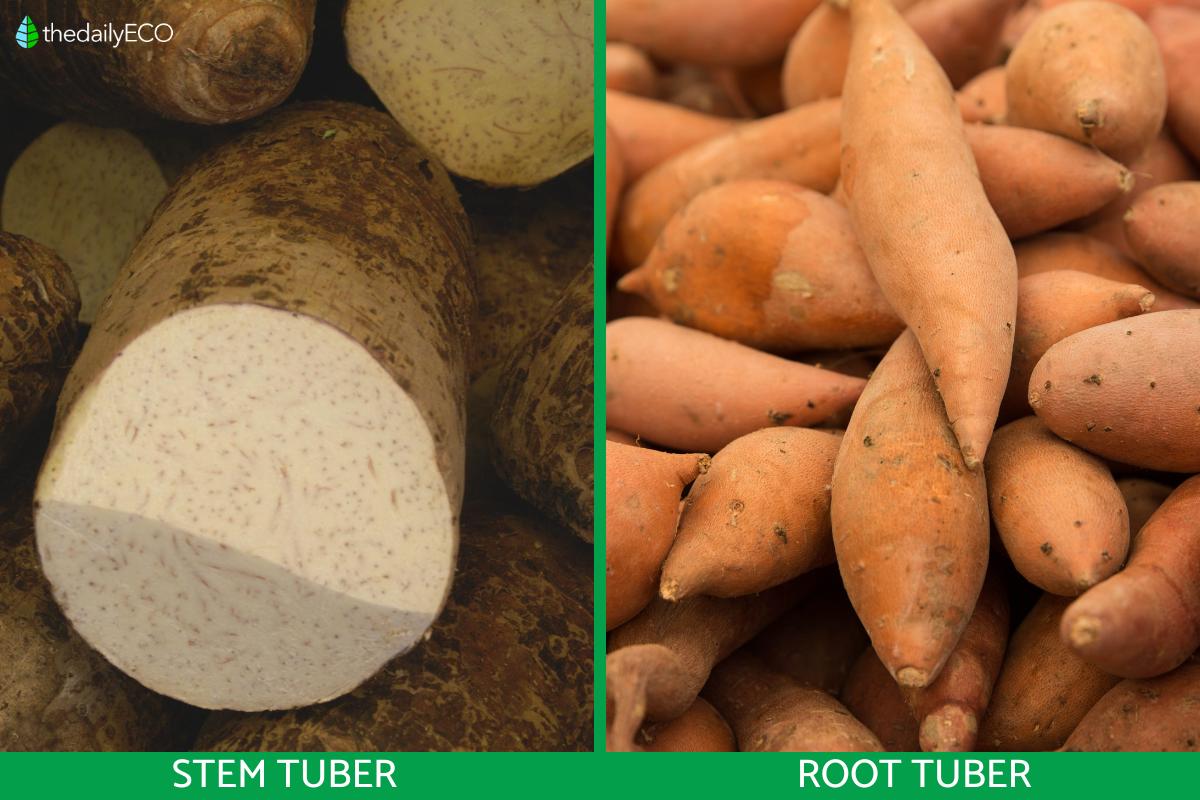
- Root tubers
- Stem tubers
These tubers are often used for less adventitious periods such as during winter or when there is a lack of oxygen in the soil. The tuber allows the plant to use these reserves until a more adventitious time arises. They will then store up extra nutrients.
Some of the types of tubers have become very important foods. They are very nutritious and often an economically important crop. They usually have a high starch content, making them rich in carbohydrates and providing an excellent source of energy. There are some exceptions, meaning tubers vary in terms of nutritional value.
Types of tubers
As we have stated above, tubers are divided into two main types. They are:
Stem tubers
These are thickened parts of the root which send nutrients along the root system to the rest of the plant. They can be located at the end or the middle of the root, depending on the plant species. They often have more than one tuber present, but it is possible to have a single root tuber in some plants. They are perennating, meaning they help the plant survive during winter or other less adventitious periods.
Root tubers
These are thickened parts of the stem, but they only develop underground. They are formed from thickened stolons or rhizomes, depending on the plant. They are often located near the surface of the soil. They are also perennated storage organs and can be found in single or multiple amounts.
Learn more about the importance of rhizomes with our article on asexual reproduction in plants.

Tuber vs. bulb differences
Bulbs are another plant structure which are used to store nutrients for growth of the plant. While they share certain similarities with tubers, they are not the same type of plant. The following are some of the differences between tubers vs. bulbs:
- Structure: the tuber is a solid structure which contains the plant tissues used to reserve nutrients. They are part of the root or stem and do not contain the entire shoot system. New shoots can develop from the eyes of the tuber, but bulbs have a develop shoot system within. Bulbs are fleshy storage structures which are layered and contain scales. Roots grow downwards from the basal plate of the bulb, but tubers do not do this.
- Direction: tubers store nutrients and grow in structures which have a horizontal direction. Bulbs have roots which grow vertically down from the basal plate.
- Depth: tubers grow underground, although some stem tubers may have some part above the soil. Bulbs have shoots which grow out of the top and above the soil.
As you can see, they are very similar. Both bulbs and tubers are used to store nutrients which can help them survive during periods of dormancy or non-adventitious circumstances. Their differences lie in their structure, type of growth and the species to which they belong.
You may have also heard of root vegetables which differ slightly from the description of a tuber. Root vegetables are any type of edible plant root which are eaten like vegetables. These include carrots and parsnips which are not types of tuber. Some tubers are root vegetables, but not all root vegetables are tubers.
Discover more types of root vegetables and tubers with our article on the best plants to grow in the fall.
Examples of plant tubers
Of all the plants with tubers, some of the best known are those we often use as food. These include the potato and yucca, the former of which is used to make everything from silky mash to crispy fries. However, the tuber structure is present on many different plants. They include the following:
- Sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas)
- Potato (Solanum tuberosum)
- Yam (Dioscorea spp.)
- Olluco (Ullucus tuberosus)
- Mashua (Tropaeolum tuberosum)
- Jicama (Pachyrhizus erosus)
- Arracacha (Arracacia xanthorrhiza)
- Chufa (Cyperus esculentus)
- Jerusalem artichoke or tupinambo (Helianthus tuberosus)
- Chinese artichoke (Stachys affinis)
- Yucca or cassava (Manihot esculenta)
- Taro (Colocasia esculenta)
- Water chestnut (Eleocharis dulcis)
- Arrowroot (Maranta arundinacea)
- Earthnut pea (Lathyrus tuberosus)
- Apios or groundnut (Apios americana)
- Spur flower (Plectranthus spp.)
- Mashua (Tropaeolum tuberosum)
Below, we look at some of the most representative types of tuber:
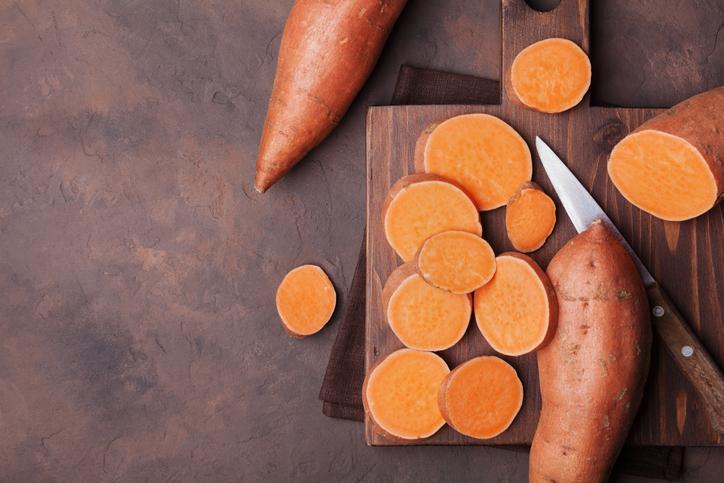
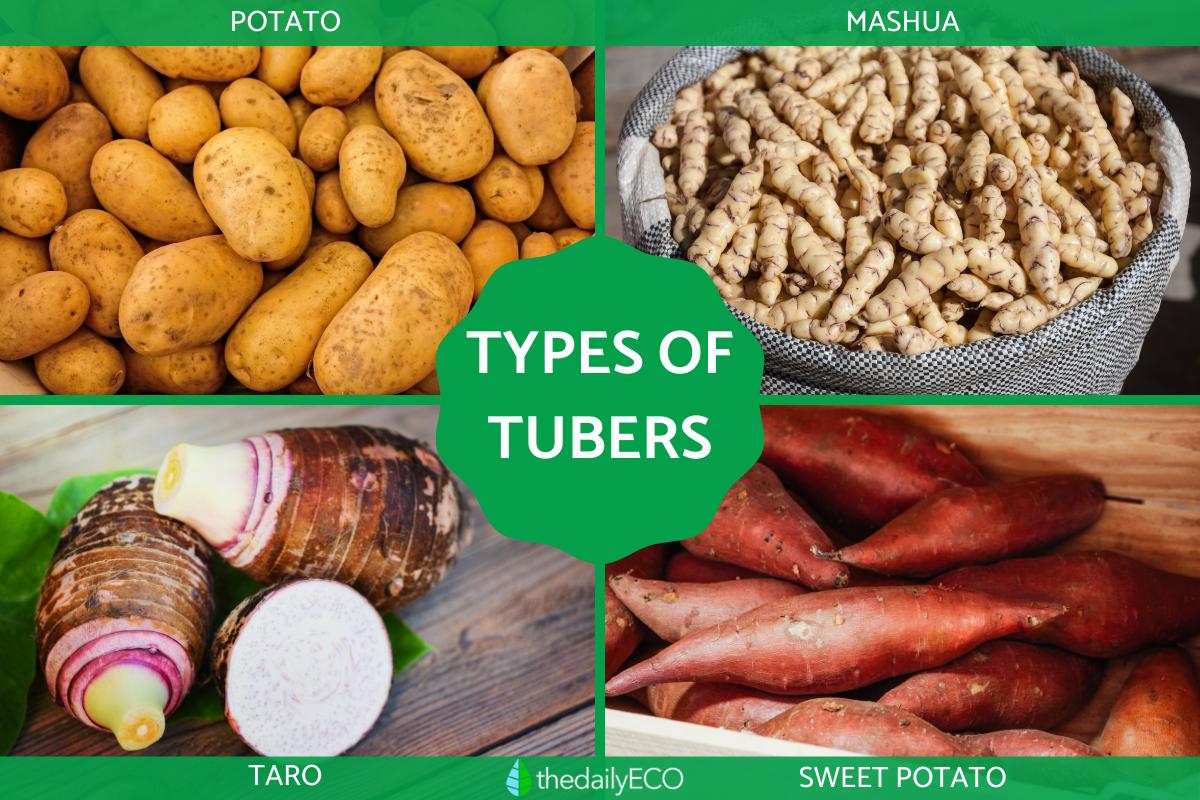
Sweet potato
Although called sweet potatoes, they are not of the same order as potatoes. Both are types of tuber which originate in South America, but the sweet potato has a much sweeter flavor. This is due to containing more sugars. They are sometimes referred to as yams, but they are not true yams. True yams are from the genus Dioscorea. They can range in shades of white or orange, depending on the variety.
Take a loot at our related article on the types of sweet potato.

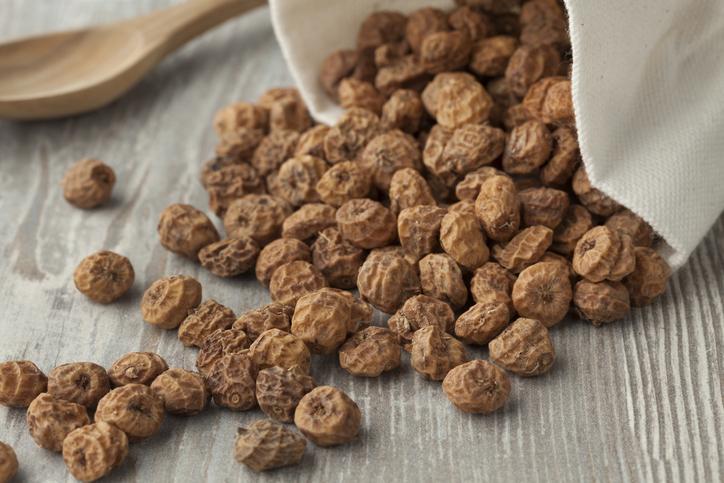
Chufa
This tuber is also called tiger nut (Cyperus esculentus) and is especially valued in parts of Europe, Africa and the Middle East. Its flavor is sweet and starchy. Although it can be consumed raw, it is much more popular used as an ingredient in tiger nut horchata, a highly valued drink in various regions.

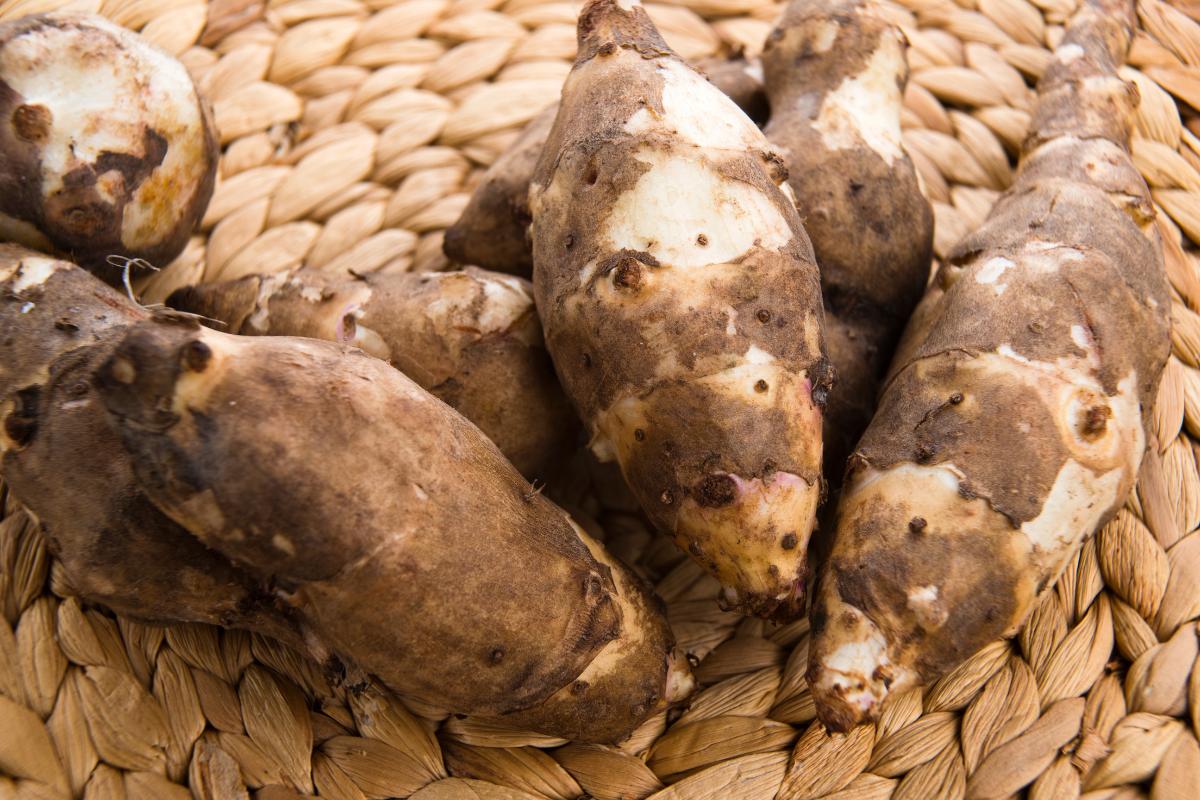
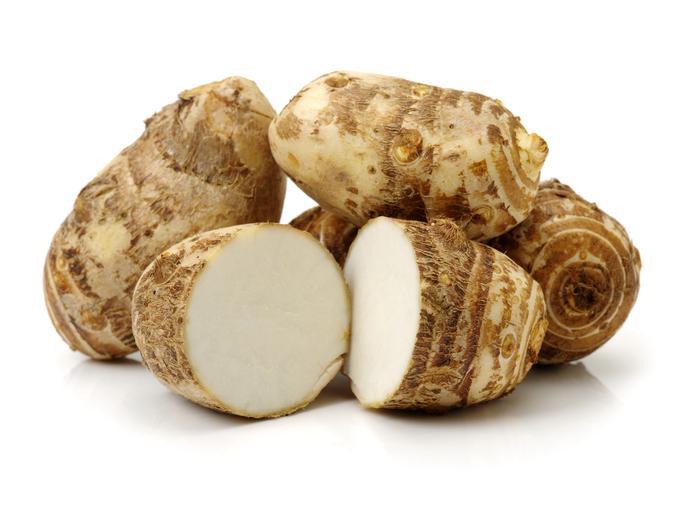
Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus)
Despite their name, they are not related to the globe artichoke (Cynara cardunculus) which is known for its layered leaves and edible heart. The Jerusalem artichoke is a type of tuber which is similar in appearance to a potato, but its flavor is nuttier and sweeter. Unlike potatoes, Jerusalem artichokes contain their energy in the form of inulin as opposed to starch. This makes them healthier and they can be eaten raw, although they are usually cooked.

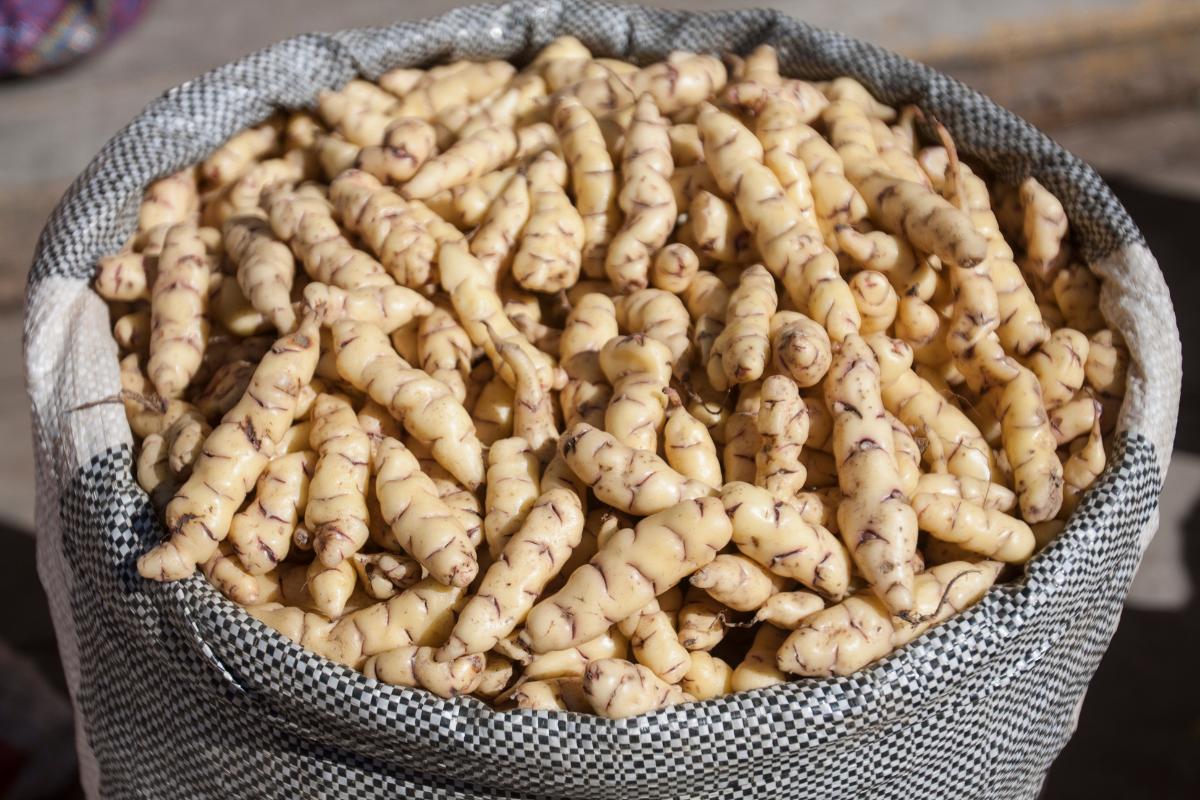
Mashua
Another tuber eaten as a root vegetable, the mashua refers to a range of edible tubers which are cultivars of the species Tropaeolum tuberosum. Although they are very bitter if eaten raw, they are one of the healthiest foods in the world. They are full of protein, healthy fatty acids and dietary fiber. They also have relatively high levels of vitamins and minerals. Its bitterness reduces with cooking.

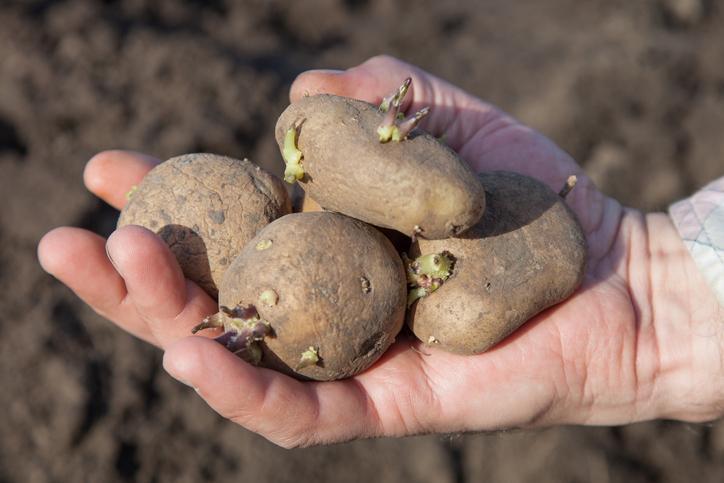
Potato
There are few tubers as international and well-known as the potato. Originally from the Andes, the potato (Solanum tuberosum) is currently one of the most widespread foods on the planet. In fact, it is the fourth most cultivated food crop in the world. There are countless varieties with adapted characteristics and they are used for a wide range of dishes. Despite being linked to cultures such as those of Celtic Ireland, they originated from South America.

Yam
The yam refers to various types of tuber from the genus Dioscorea. Two of the most common are the white yam (Dioscorea rotundata) and the yellow yam (Dioscorea cayenensis). Its origin lies in Africa and it is a starchy tuber whose name means ‘to eat.’ In Africa, it has been consumed since prehistoric times and is currently widely spread, especially in South America.

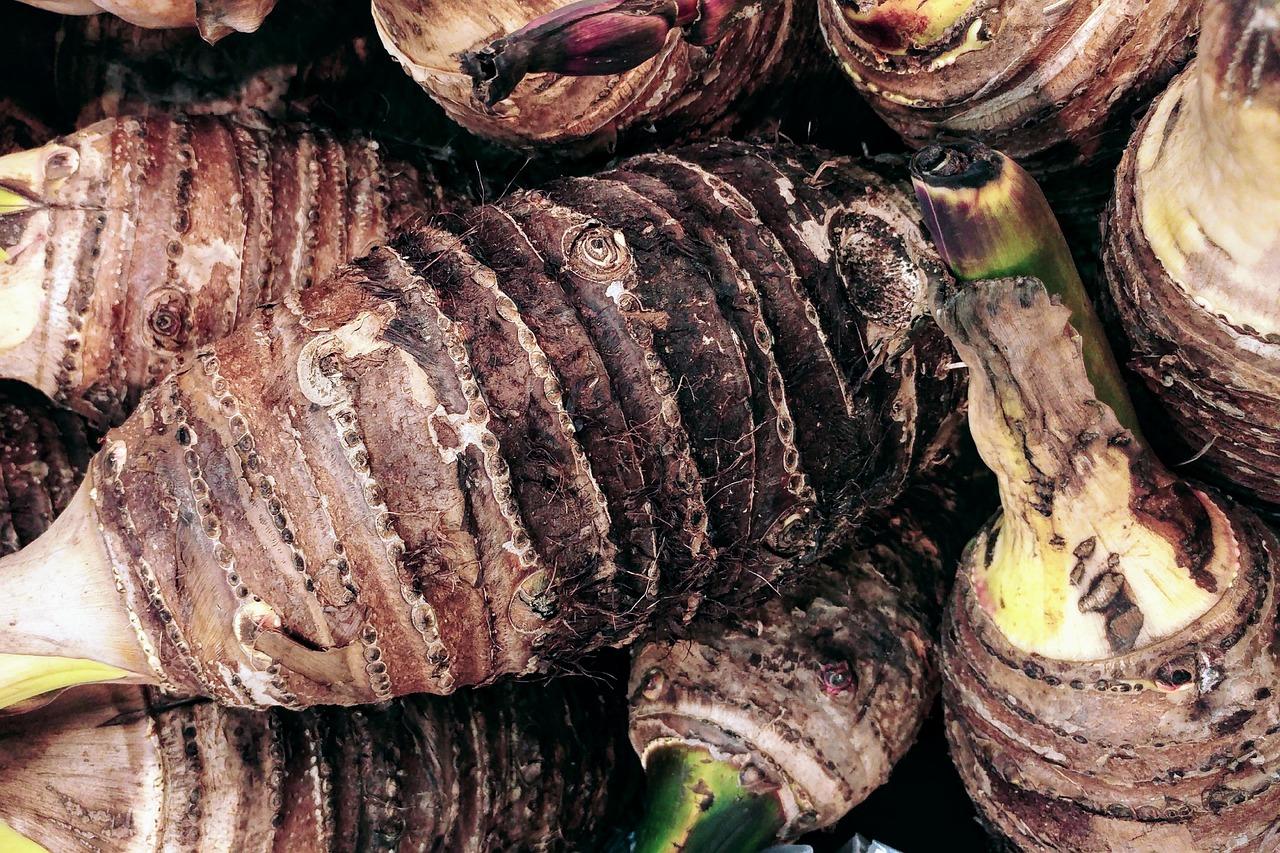
Taro
Although not as popular in Europe as it is in other parts of the world, taro (Colocasia esculenta) is the fifth most cultivated tuber globally. It has a multitude of names depending on local culture, but taro is the most recognized in English. It is very starchy and has little protein. It does have a high carbohydrate content and its edible leaves are full of vitamins. It is toxic raw, but when prepared it can be used to make a wide range of foodstuffs from various cultures.

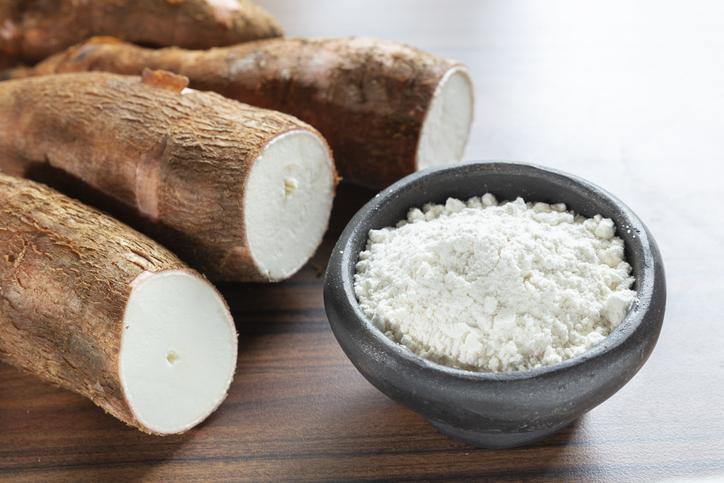
Yucca
Also known as cassava, the yucca (Colocasia esculenta) is another widely used tuber that has its origin in South America. Its skin is hard and woody in appearance, but its meat is white and starchy. It is a very important source of carbohydrates in many tropical areas of Asia, America and Africa. It is also toxic raw, so it needs to be cooked or processed. Its starch is highly valued and it can be used to make a wide range of products, including biofuel.

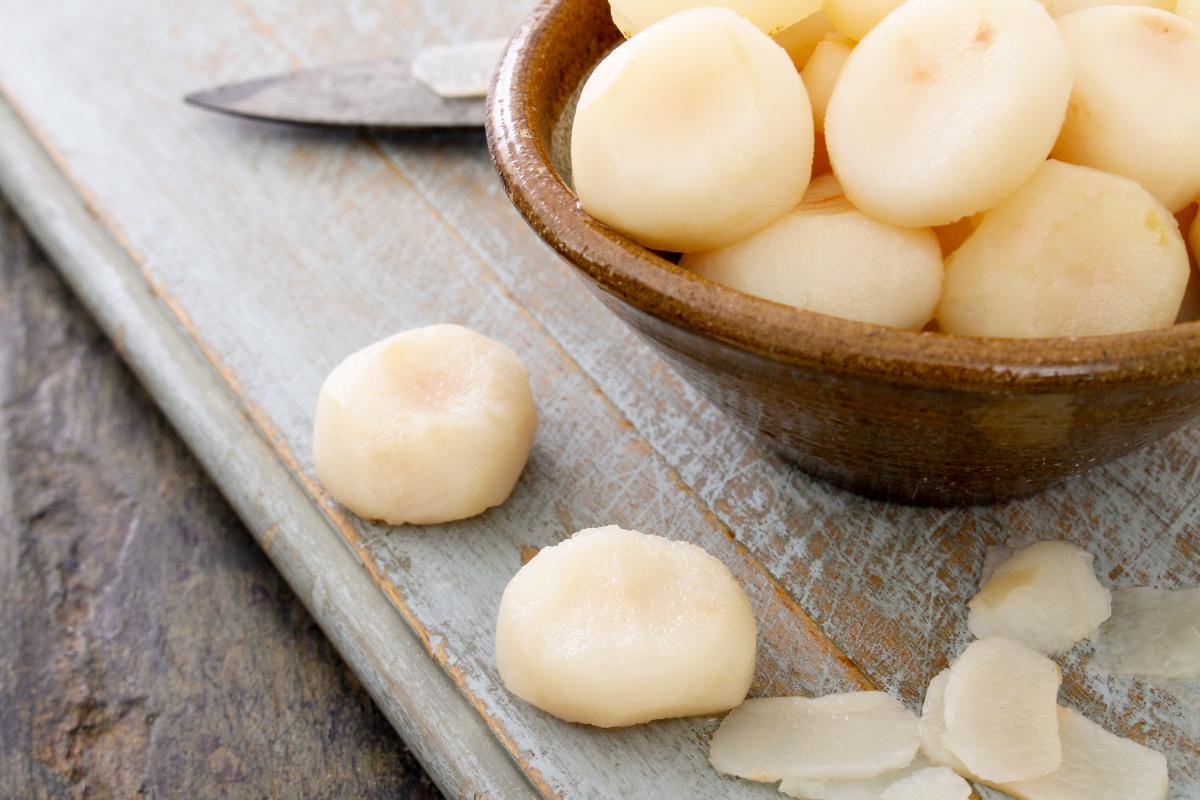
Water chestnut
Also known as the Chinese water chestnut (Eleocharis dulcis), this is a relatively small tuber which is enjoyed particularly in Chinese and Asian cuisine. They can be eaten raw when they are sweet. They have a crunchy texture, although this is reduced when cooked.
Learn about a type of non-edible tuber with our guide to caring for caladium plants.

If you want to read similar articles to What Are Tubers in Plants?, we recommend you visit our Plant care and cultivation category.