What Are Tepals in a Flower?


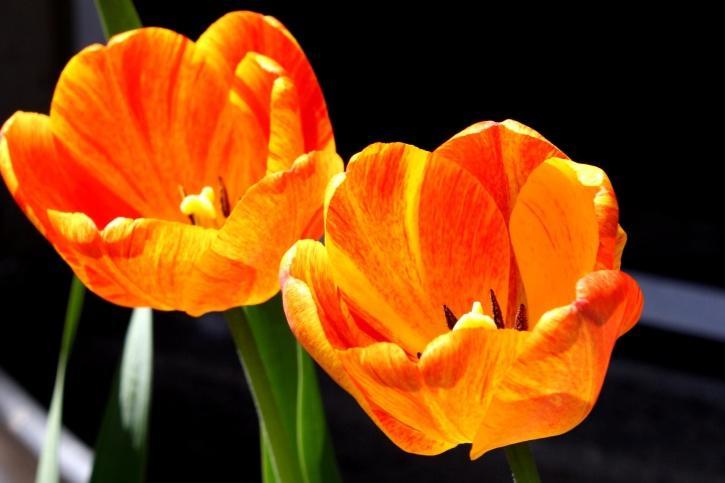
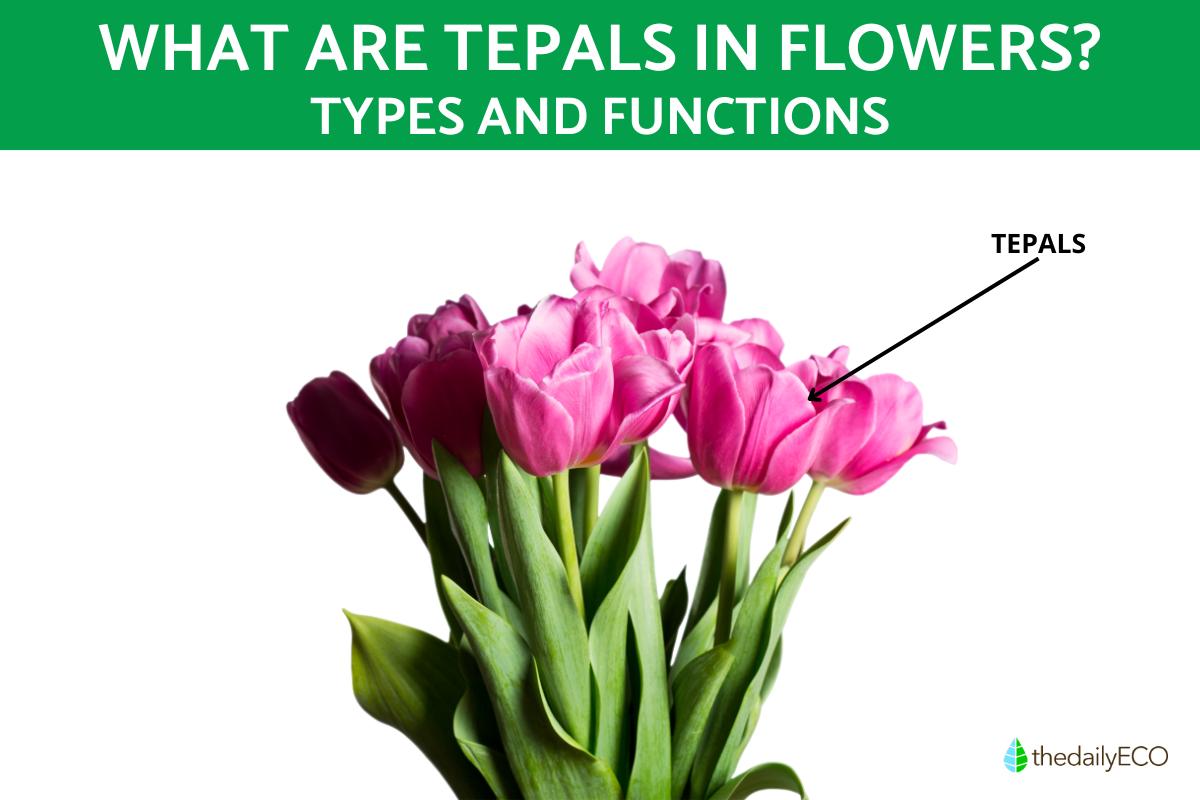
Ever admired a rose up close and then compared it to a tulip? Unlike most flowers, the colorful parts of a tulip aren't classic petals, but rather structures called tepals. While petals are the usual colorful attractors for pollinators, some flowers, like tulips or lilies, have these unique tepals. Tepals blur the lines between petals and sepals, combining their functions into a single structure that plays a vital role in plant reproduction.
This article by thedailyECO explores what tepals are, how they differ from their petals and sepals, and the diverse functions they fulfill in the plant kingdom.
What are flower tepals?
The petals and sepals are two external parts of the flower found in the perianth. The perianth is the non-reproductive part of the flower and consists of two layers: the outer layer (sepals) and the inner layer (petals). Their main function is to protect the reproductive organs of the plant, which are located at the center of the flower.
Sepals are typically green and resemble leaves. They form the outermost layer of the flower and enclose the flower bud before it opens, providing protection to the developing flower. Once the flower blooms, sepals can sometimes be seen at the base of the petals.
Petals, on the other hand, are usually more colorful and conspicuous than sepals. They form the second layer of the perianth and are designed to attract pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, and birds. The bright colors and distinct shapes of petals play a crucial role in the plant's reproductive process by luring pollinators to the flower.
When sepals and petals cannot be easily distinguished from each other, they are collectively referred to as tepals. Tepals are the undifferentiated, leaf-like structures that surround and protect the reproductive organs of the plant. This occurs when both the sepals and petals look alike in color and shape, making it difficult to tell them apart.
Tepals are common in monocotyledonous plants, often referred to as monocots. Monocots are a group of flowering plants that have one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon, in their seeds. Examples of monocots include magnolias, lilies, daffodils, and tulips. These plants often have flowers with tepals instead of distinct sepals and petals.
Additionally, tepals are typical of primitive plants. Primitive plants are those that have not evolved highly specialized structures. In these plants, the absence of differentiated sepals and petals suggests that attracting pollinators was not as critical to their survival. This can be seen in early flowering plants that relied more on wind or water for pollination rather than animal pollinators.

Functions of the tepals
The main function of tepals is to protect the reproductive organs of the plant. Tepals wrap around these reproductive organs, shielding them from damage caused by external agents. In environments with strong winds, heavy rainfall, or intense sunlight, the tepals' protective barrier is especially important for the plant's survival and reproduction.
Tepals also provide necessary structural support to the flower, facilitating the process of pollination. When the plant reaches sexual maturity, tepals help to attract pollinators such as insects, birds, and even the wind. Pollinators are crucial for the transfer of pollen from the male organs (stamens) to the female organs (pistils), enabling fertilization and seed production. By maintaining the integrity and accessibility of the reproductive organs, tepals enhance the efficiency of this process.
In many plant species, especially monocotyledonous plants (monocots) such as tulips and lilies, tepals replace the distinct sepals and petals found in more evolved plants (dicotyledonous plants or dicots). Tepals provide both aesthetic appeal and functional support, making them essential components of the flower. Their similar appearance to petals can attract pollinators.
Difference between petals and tepals
The key difference between petals and tepals lies in how well-defined the flower parts are for the roles of attracting pollinators and protecting the bud.
Dicotyledonous plants (dicots), commonly referred to as plants with two seed leaves, typically have a well-defined floral structure. Here, petals are the brightly colored structures found in the corolla, the inner whorl of modified leaves. Their main function is to attract pollinators. These pollinators, often insects or birds, are drawn to the vibrant colors and may even be rewarded with nectar, a sugary substance produced by the flower.
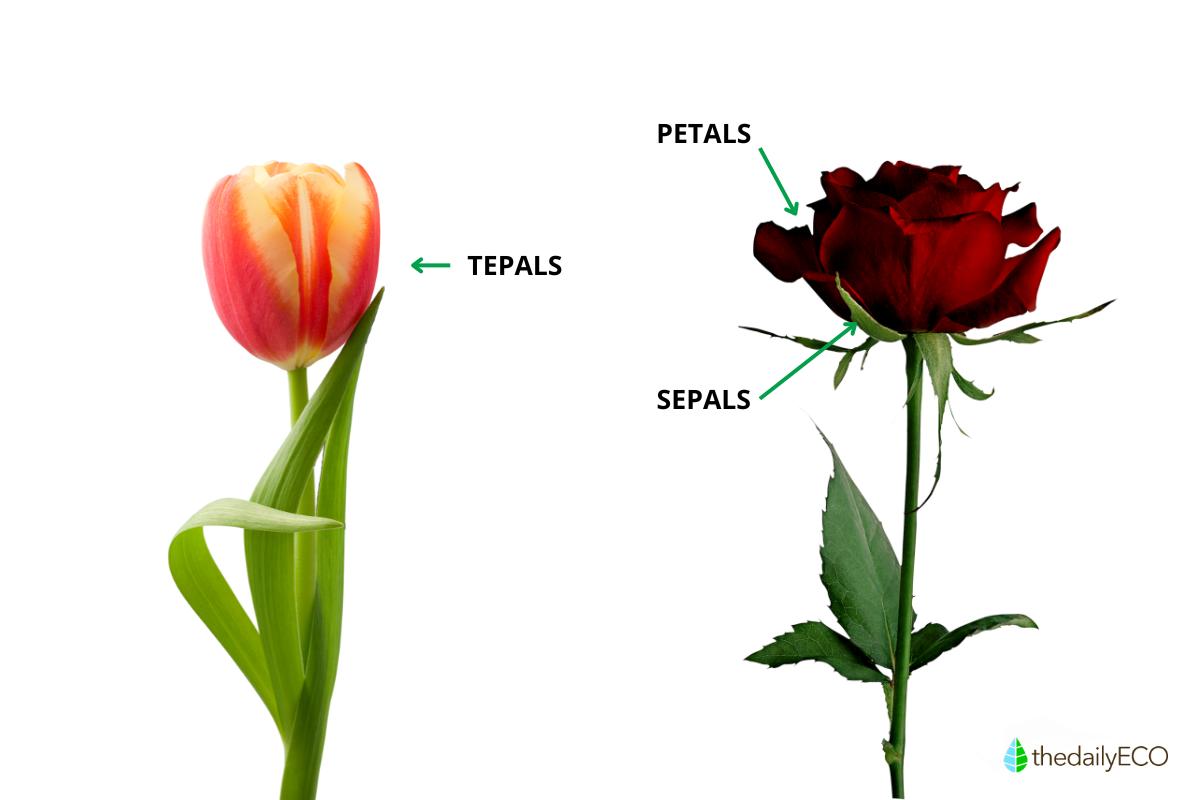
Sepals, on the other hand, form the calyx, the outermost whorl. They are usually green and leaf-like, acting as a protective shell for the developing bud inside the flower before it blooms. A classic example of this clear distinction is the rose - the vibrant red petals are easily differentiated from the green, supporting sepals.
Monocotyledonous plants (monocots), plants with one seed leaf, often lack the clear separation between petals and sepals seen in dicots. Here's where tepals enter the scene. Tepals are single structures found in the perianth, the non-reproductive part of the flower, that fulfill the combined function of both petals and sepals.
They can be brightly colored like petals to attract pollinators, green like sepals for protection, or even somewhere in between. Unlike roses with well-defined petals and sepals, a tulip exemplifies a flower with tepals. The colorful flower of a tulip emerges directly from the stem without separate green sepals.
Tepals tend to be sturdier and more robust than petals, offering additional protection to the flower's reproductive organs inside. Petals, conversely, are typically lighter and more delicate, allowing them to unfurl easily and showcase their vibrant colors to attract pollinators.
Our other article explores what the functions of sepals in a flower are, revealing their crucial role in flower development and protection.

Types of tepals
Tepals exhibit great diversity in their appearance and morphology. Botanists classify tepals primarily based on their visual characteristics, such as color, shape, texture, and arrangement. This classification provides insights into the evolutionary history and ecological adaptations of plants.
- Color: tepals can come in a wide range of colors, including white, yellow, pink, red, purple, and blue. Some plants have tepals of uniform color, while others exhibit patterns, gradients, or even multiple colors on each tepal.
- Shape: the shape of tepals varies significantly among different plant species. They can be lanceolate, ovate, elliptical, linear, spatulate, or various other forms. Some tepals are narrow and elongated, while others are broad and rounded.
- Texture: tepals may have diverse textures, ranging from smooth and glossy to hairy or textured. The texture can play a role in attracting specific pollinators or providing protection against environmental stressors.
- Arrangement: tepals can be arranged in different configurations, including overlapping, spreading, reflexed, or fused. The arrangement of tepals influences the overall appearance of the flower and may impact pollination dynamics.
Our other article, dives deeper into what the stamens of a flower are, revealing how stamens and other structures work together to ensure plant survival.
Examples of plants with Tepals
Here are some examples of plants with different types of tepals:
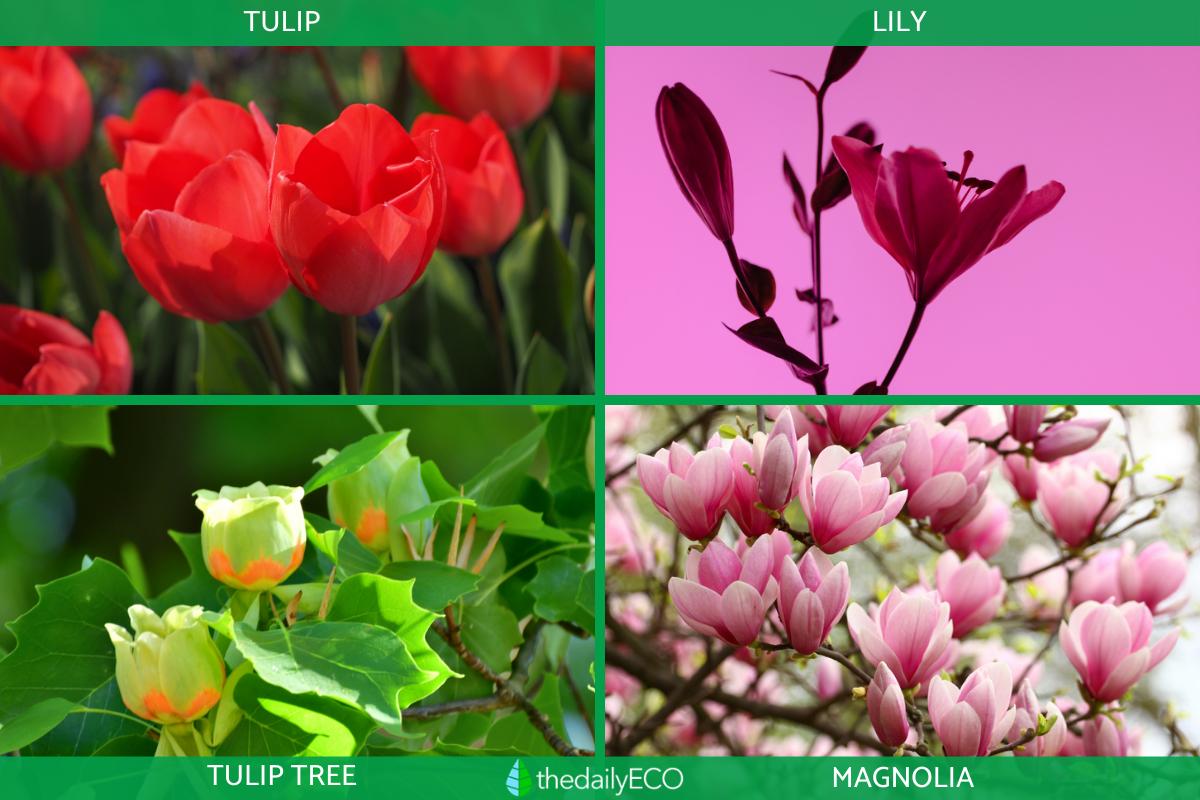
Tulip (Tulipa spp.)
Tulips are renowned for their showy flowers with six tepals arranged in a cup-shaped formation. The tepals often exhibit vibrant colors and various patterns, attracting pollinators such as bees and butterflies.
Lily (Lilium spp.)
Lilies possess six tepals that are often large and trumpet-shaped. The tepals may be fragrant and display an array of colors, including white, pink, orange, and yellow. The distinct shape and coloration of lily tepals contribute to their allure in gardens and floral arrangements.
Tulip Tree (Liriodendron tulipifera)
The tulip tree produces unique flowers with yellow-green tepals that resemble tulips. Each flower has six tepals arranged in a star-shaped pattern, attracting bees and hummingbirds for pollination.
Magnolia (Magnolia spp.)
Magnolias are known for their large, fragrant flowers with tepals that vary in shape and color. Some magnolia species have tepals that are elongated and narrow, while others have broad, petal-like tepals with a waxy texture.

If you want to read similar articles to What Are Tepals in a Flower?, we recommend you visit our Biology category.