What Are Photosynthetic Pigments?

Photosynthesis is a necessary process for most life on Earth, including ourselves. Without it, ecosystems would collapse and only certain prokaryotic organisms which do not rely on it would be able to continue. Photosynthetic organisms include most plants, as well as certain types of algae and bacteria. Although no animals are capable of photosynthesis, all complex organisms rely on it for survival. This means photosynthetic pigments are vital for life on Earth as we know it. These are molecules which allow light energy to be converted into chemical energy, this energy being necessary for various metabolic processes.
At thedailyECO, we ask what are photosynthetic pigments? In addition to understanding what photosynthetic pigments do, we look at the types and examples which can be found in nature.
What are photosynthetic pigments?
There are various biological pigments in nature which carry out different purposes. Also known as biochromes, these are pigments which are produced by living organisms. This is in contrast to certain types of pigments found in minerals, rocks or other inorganic materials. Photosynthetic pigments are specifically those that are able to capture light energy to allow the process of photosynthesis to be carried out.
All light is an electromagnetic wave. Visible light is the light at a wavelength our eyes can detect. It is made up of the rainbow spectrum of colors, but this is only a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Specifically it refers to those which are visible at wavelengths between 700 and 400 nm. Among the wavelengths present in visible light is red light, the one with the lowest energy. Blue light contains the most energy since it is the shortest wavelength. Sunlight appears white at first, but when we pass it through a prism, it splits into all the components of the visible spectrum.
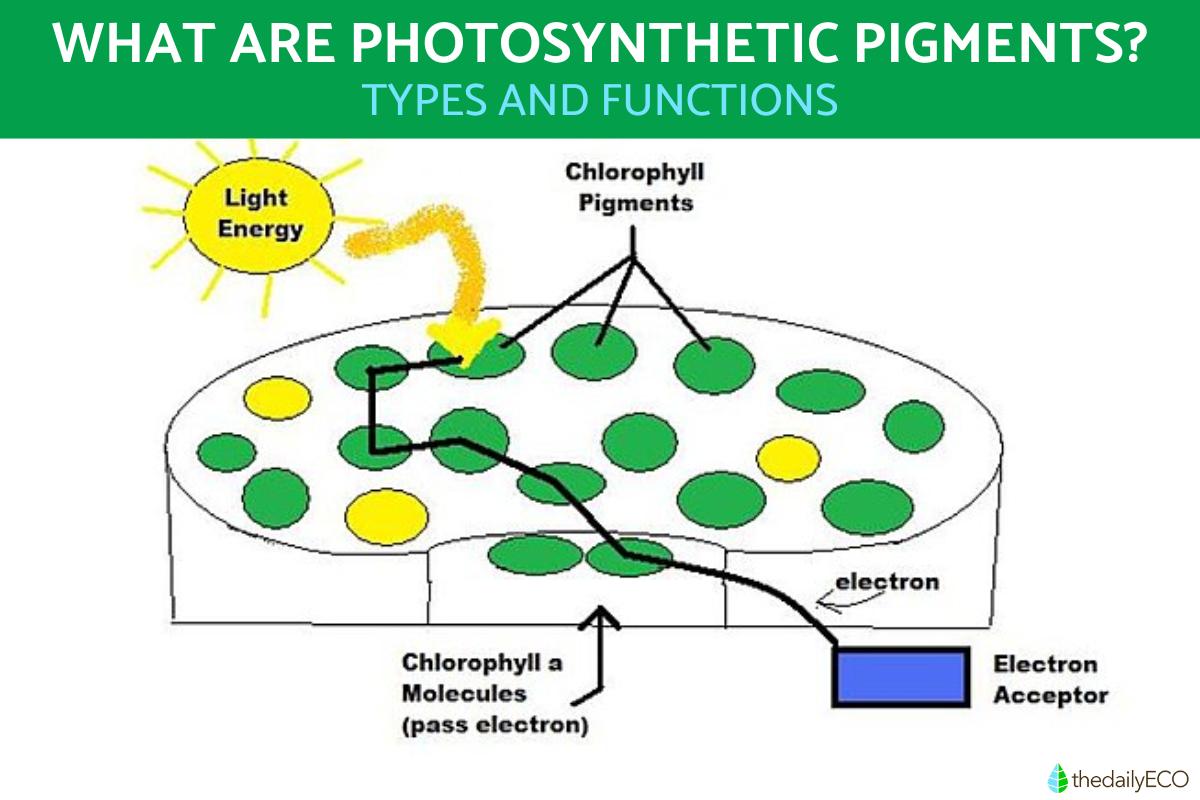
This explanation is necessary to understanding what photosynthetic pigments are. When most substances receive sunlight, they absorb some wavelengths and reflect others. We see things in the color of the wavelength they reflect, while the rest of the energy is absorbed as heat.
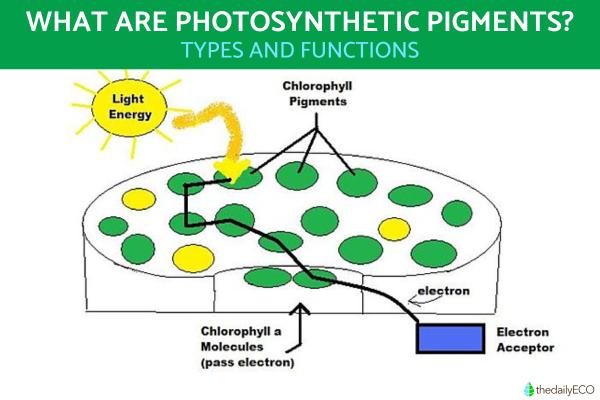
Photosynthetic pigments are able to capture light because they are molecules which carry out a process of photoexcitation. This is when the photons in specific wavelengths of light excite the electrons of photosynthetic pigments. These excited electrons are then transferred to the reaction center to be converted into sugars. Once this happens, the photosynthesis will be complete.
You can learn more about this process of light conversion in our article explaining how does photosynthesis work?
Photo: Slideshare
Characteristics of photosynthetic pigments
The main characteristic of photosynthetic pigments is their ability to absorb light, which the process of photosynthesis will convert into chemical energy. This chemical energy is in the form of sugars that can be assimilated by the plant or similar photosynthetic organism. In addition to plants which carry out photosynthesis, there are also photosynthetic pigments in algae and some bacteria.
In plants, photosynthetic pigments are found in the chloroplasts. These are types of organelles found within plant cells. In bacterial cells, the photosynthetic pigments are found in chromatophores. These are organelles which are found in certain types of bacteria, but not all.
The different colors of photosynthetic pigments give them the ability to absorb and reflect different wavelengths of light. Photosynthetic organisms with a greater diversity of pigments can absorb energy from a wider variety of light types.
The phase of photosynthesis in which photosynthetic pigments are useful is the first phase. Known as the light phase, this is where the pigments capture light and absorb the energy of the photons within. The rest of the photosynthetic process will ultimately convert this into the nutrients and energy needed by the photosynthetic organism.
Find out more about the organelles which contain photosynthetic pigments with our articles asking what is a chloroplast and what are chromatophores?
Types of photosynthetic pigments with examples
As we have stated, different types of photosynthetic pigments can absorb different wavelengths of light. This is because they can absorb light more efficiently in certain parts of the spectrum.
Chlorophyll
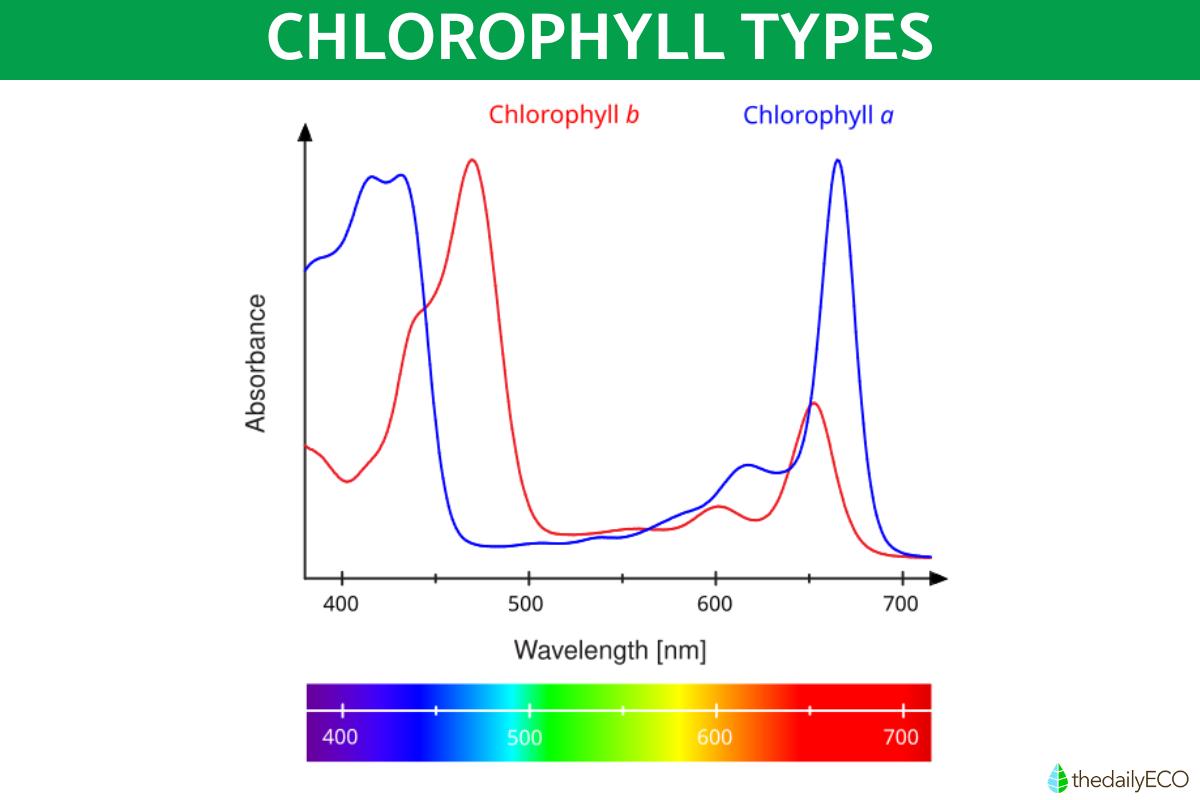
The primary photosynthetic pigment is chlorophyll, but even this is classified into different types. Although various types of chlorophyll are used in photosynthesis, each can be found in various organisms and are better at capturing different types of light. For example:
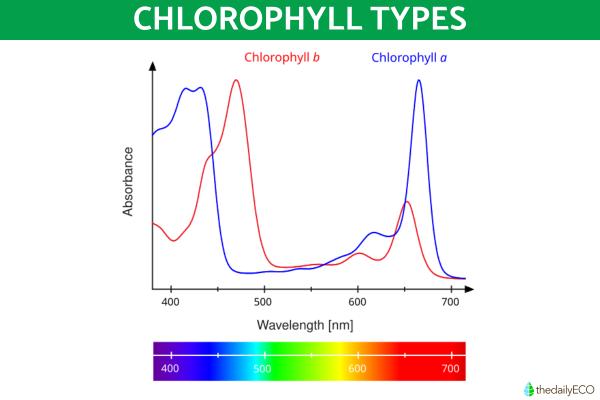
- Chlorophyll a: found in plants, algae and cyanobacteria. Able to capture violet-blue and red light the best.
- Chlorophyll b: an accessory pigment in plants and algae which also helps to capture blue and yellow-orange light.
- Chlorophyll c: another accessory pigment found in diatoms and brown algae which helps capture blue-green light.
- Chlorophyll d: found in red algae and some cyanobacteria and captures far-red light.
- Chlorophyll f: absorbs near-red light in some cyanobacteria.
One of the reasons different organisms have different types of chlorophyll is their location. Water filters out light, so some algae and cyanobacteria will not need certain chlorophylls and will make better use of others. They help the organisms to broaden their absorption spectrum.
We explain more about the types and functions of chlorophyll in our related guide.
Carotenoids
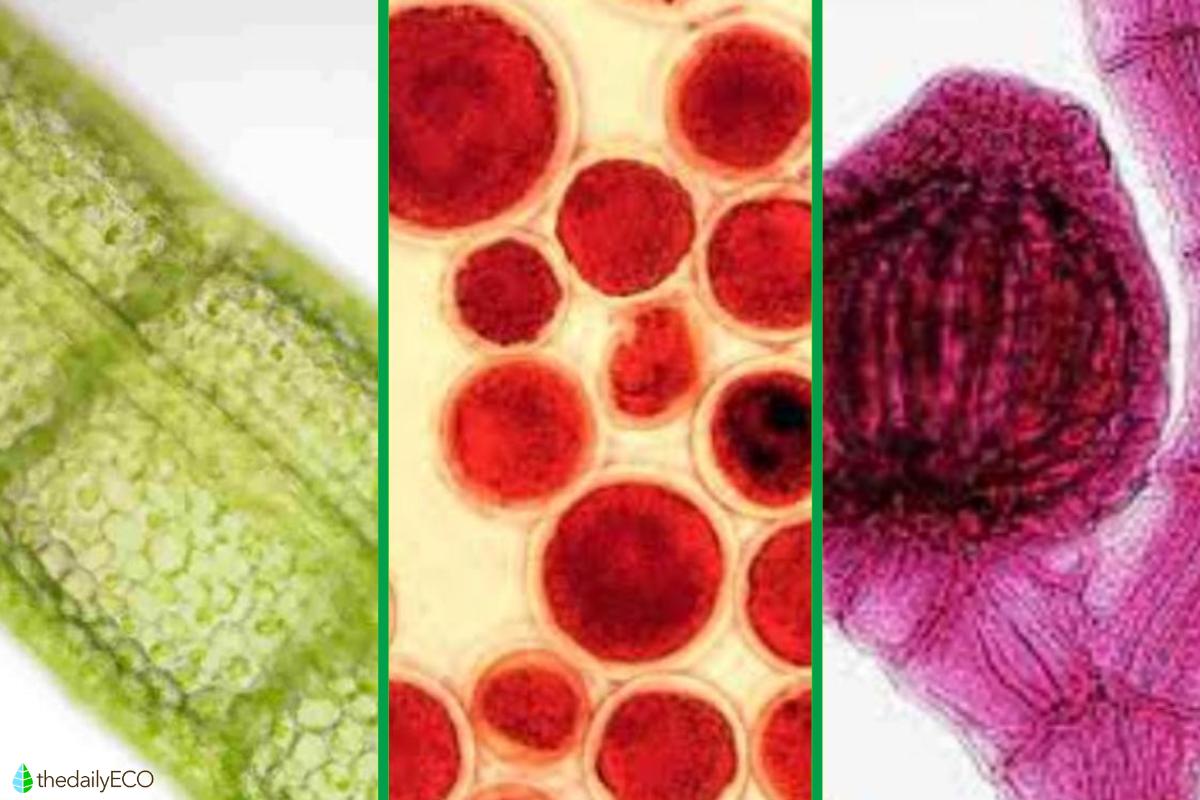
Unlike chlorophylls, which are green, carotenoids are red, yellow and orange in color. This coloration is due to their ability to absorb violet and blue-green light. In addition to absorbing light, they perform the important function of giving fruits or seeds their bright colors. This helps to attract animals and promote seed dispersal, another vital process for ecosystems.
Another vital function performed by carotenoids is the elimination of excess energy that the plant receives from the sun. After absorbing it, they dissipate this energy as heat. They can be classified into two subtypes: carotenes and xanthophylls. The former give yellow, orange, or red colors, while the latter are always yellow.
Phycobilin
Phycobilins are photosynthetic pigments found only in red algae and cyanobacteria. They are of great importance in research, being used as chemical labels due to the characteristic fluorescence they emit when exposed to intense light.
You can learn more about red algae with our article asking what causes red tide?

If you want to read similar articles to What Are Photosynthetic Pigments?, we recommend you visit our Biology category.