Types of Non-Stinging Jellyfish


Jellyfish are known for their ability to sting, maintaining this ability even when they are dead. It is a useful behavior which is used to both protect themselves from predators and catch their own prey. They are able to sting thanks to specialized cells on their tentacles called nematocysts. These cells release venom on point of contact, something which can be dangerous for humans swimming near them. Different types of jellyfish have different levels of venomousness. Some are species are non-stinging jellyfish because they have little to no venom at all.
At AnimalWised, we discover 6 types of non-stinging jellyfish that can be found in oceans around the world. We provide fun facts and photos of these jellyfish that don't sting so you can be aware if you come across one in the wild.
Are there jellyfish that don't sting?
Jellyfish are cnidarians, aquatic invertebrates which are defined by having cnidocytes, specialized explosive cells which are able to help protect against predators and catch their own prey. Inside each cell is a nematocyst, a capsule containing venom, and a coiled filament. Changes in pressure, temperature, or physical contact with potential prey can activate these cells, causing the filament to fire and release the venom from the capsule.
It is a little misleading to say there are jellyfish that do not sting at all. This is because all jellyfish have nematocysts within their cnidocyte cells as defining characteristics of their species. Despite this, it is true to say there are various harmless jellyfish. This is because the level of venom which their stinging cells contain is so low that their stings do not register on human skin.
No jellyfish will want to attack a human, but if the latter approaches the former, they will get stung if they come in contact with their tentacles. In cases of non-stinging jellyfish, the envenomation is so low as it will not usually cause a reaction. This may differ in individuals who have a sensitivity to jellyfish stings. Regardless of the ‘harmless’ jellyfish we share here, it is important you avoid all jellyfish when swimming near them.
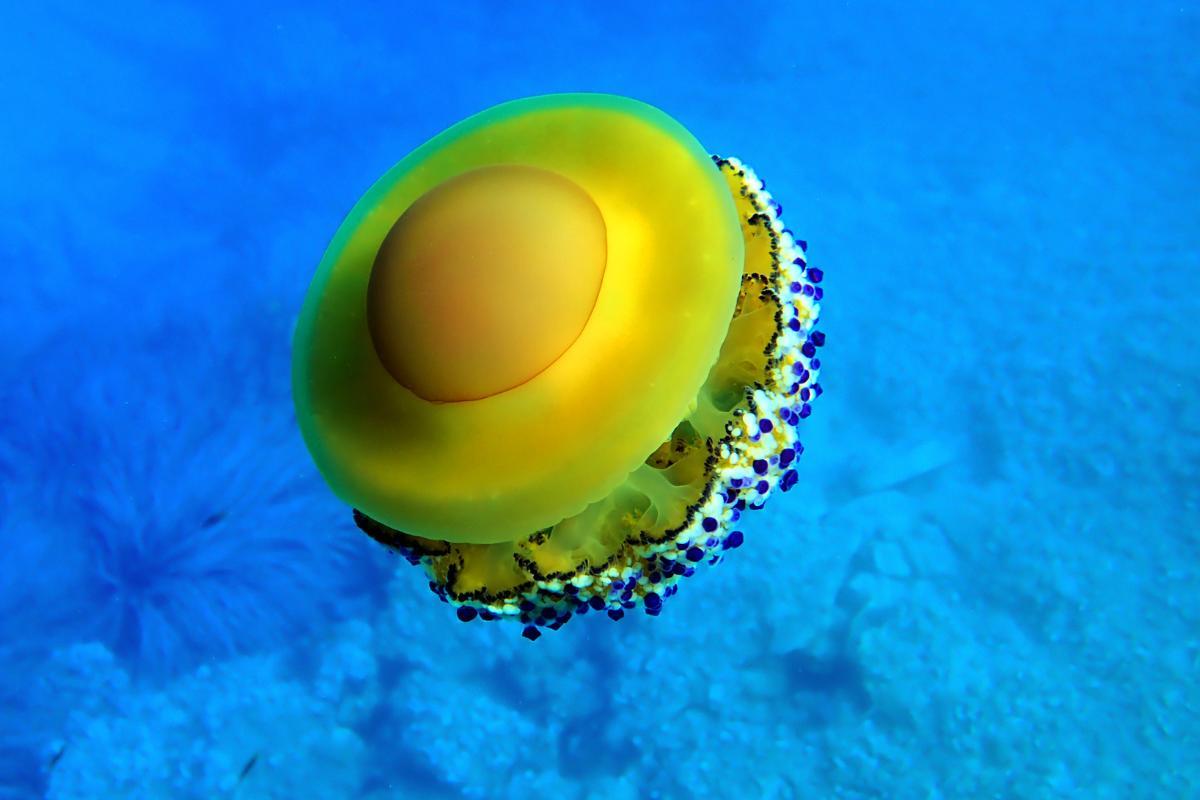
Fried egg jellyfish
Also known as the Mediterranean jellyfish, the fried egg jellyfish (Cotylorhiza tuberculata) stands out among the non-stinging jellyfish as being one of the most harmless. While it does have mild levels of venom, their sting has little to no effect on people. It is a pelagic species that lives both near the coasts and in the deep waters of the Mediterranean Sea.
Its umbrela (main body) is flattened and yellowish-brown with an central orange protuberance. These features give it an appearance similar to a fried egg when viewed from above, hence its common name. It lacks marginal tentacles, but has eight oral arms with three button-shaped appendages at their ends. It is usually accompanied by crabs and some fish that use it as shelter during their first stages of life.
Learn more with our article on whether the fried egg jellyfish is poisonous.

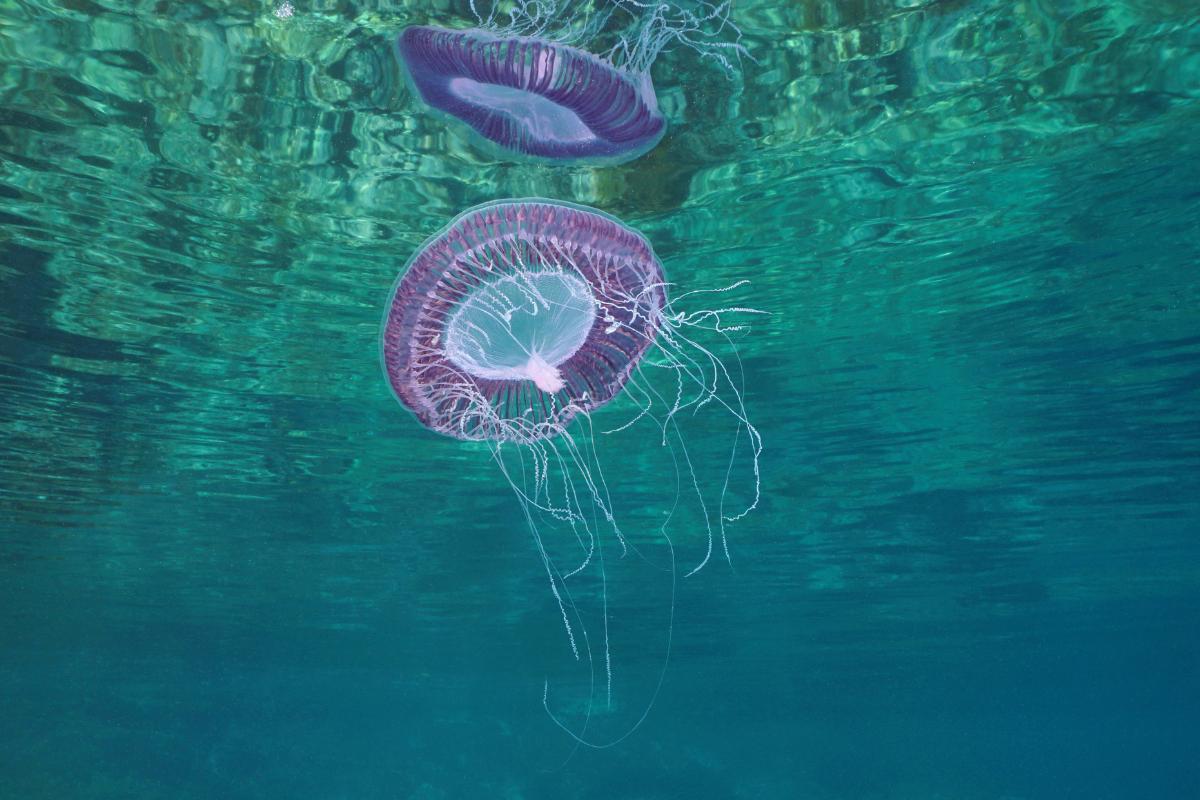
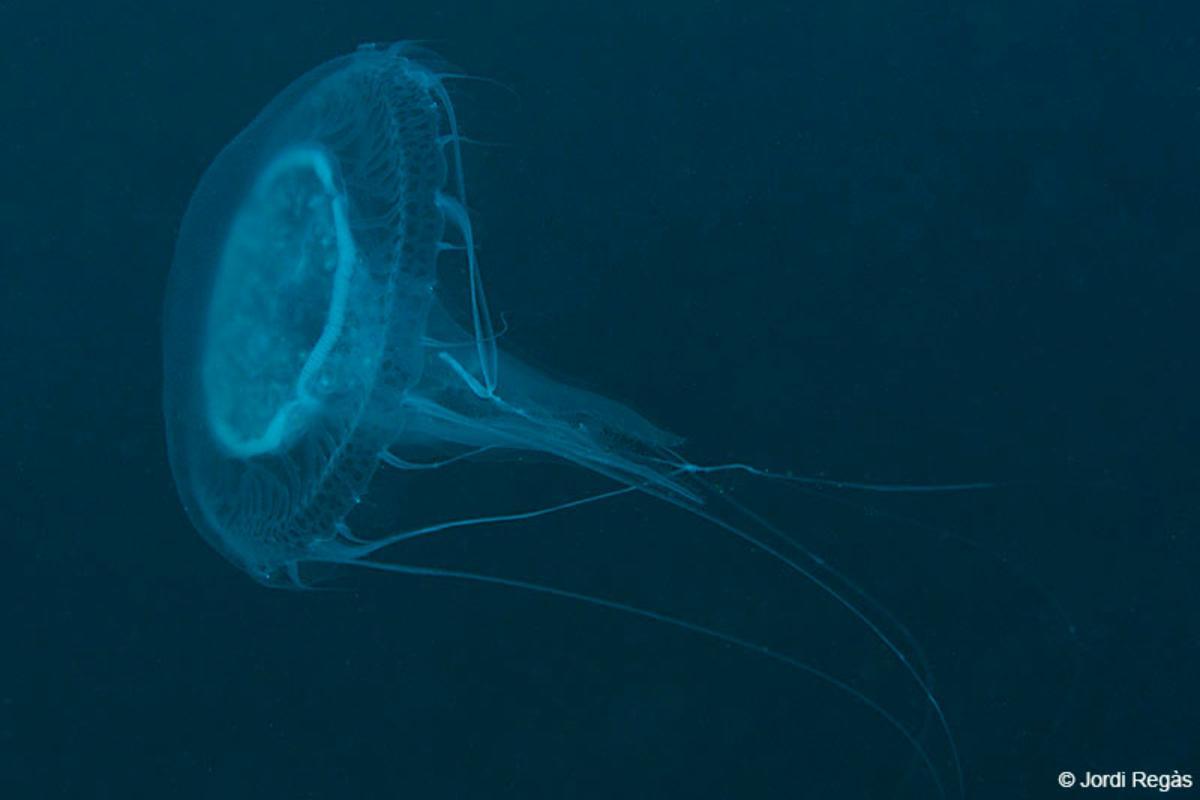
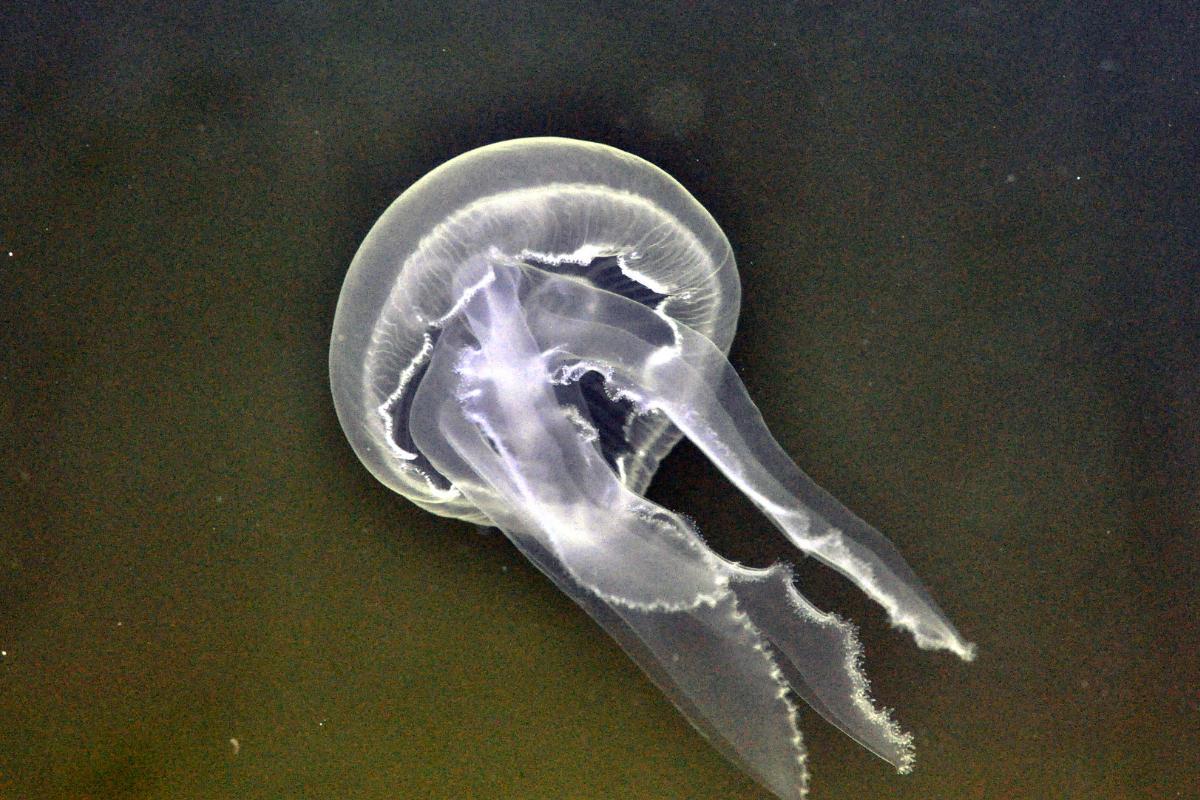
Common jellyfish
Also known as the moon jellyfish or saucer jelly, the common jellyfish (Aurelia aurita) is a relatively harmless jellyfish species with a very mild sting. It can cause some irritation, but it will not serious injure someone. It is cosmopolitan and one of the most abundant jellyfish, found in waters around the world except at the poles due to their very cold waters.
Its umbrella is flattened, transparent and can reach up to 25 centimeters in diameter. In it you can see four horseshoe-shaped reproductive organs that are whitish, yellowish or slightly pink. Its four oral arms are elongated and also have hundreds of short, thin marginal tentacles.

Many-ribbed jellyfish
Commonly known as the many-ribbed jellyfish, Aequorea forskalea is a hydromedusa classified as harmless that has a flattened, translucent umbrella with blue radial channels. Its umbrella reaches a diameter of up to 40 cm. It has a large number of fine tentacles and lacks oral arms.
It is distributed from temperate to tropical waters, mainly in coastal and littoral areas. It can occasionally appear in the open sea. It is usually common in the Spanish Mediterranean, especially during spring and can form large swarms. Species of the Aequorea genus are bioluminescent thanks to the presence of a protein called aequorin.
Learn more about how bioluminescent light works with our related article.

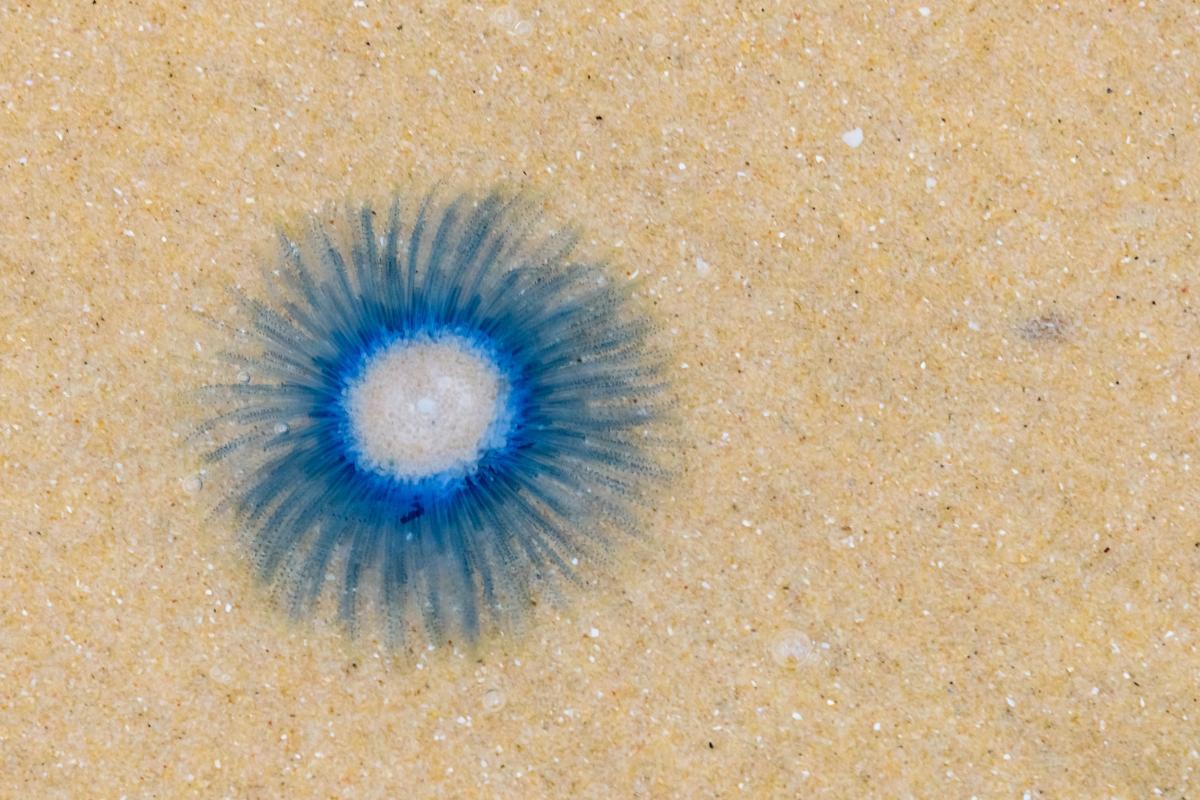
Blue button jellyfish
The blue button (Porpita porpita) is a cnidarian, but it is not a true jellyfish. It usually lives in tropical and subtropical waters of the Pacific, Atlantic and Indian Oceans, as well as in the Mediterranean Sea and towards the east of the Arabian Sea.
In general, the phase that we usually observe in their life cycle corresponds to a floating colony of polyps. Its disk can measure 5 cm and is made up of a hard float filled with gas in the center and a colony of intense blue, purple or yellow hydroids. These hydroids resemble tentacles and contain nematocysts which essentially function to same as true jellyfish. The sting of the blue button jellyfish is mildly stinging, but can cause slight skin irritation.

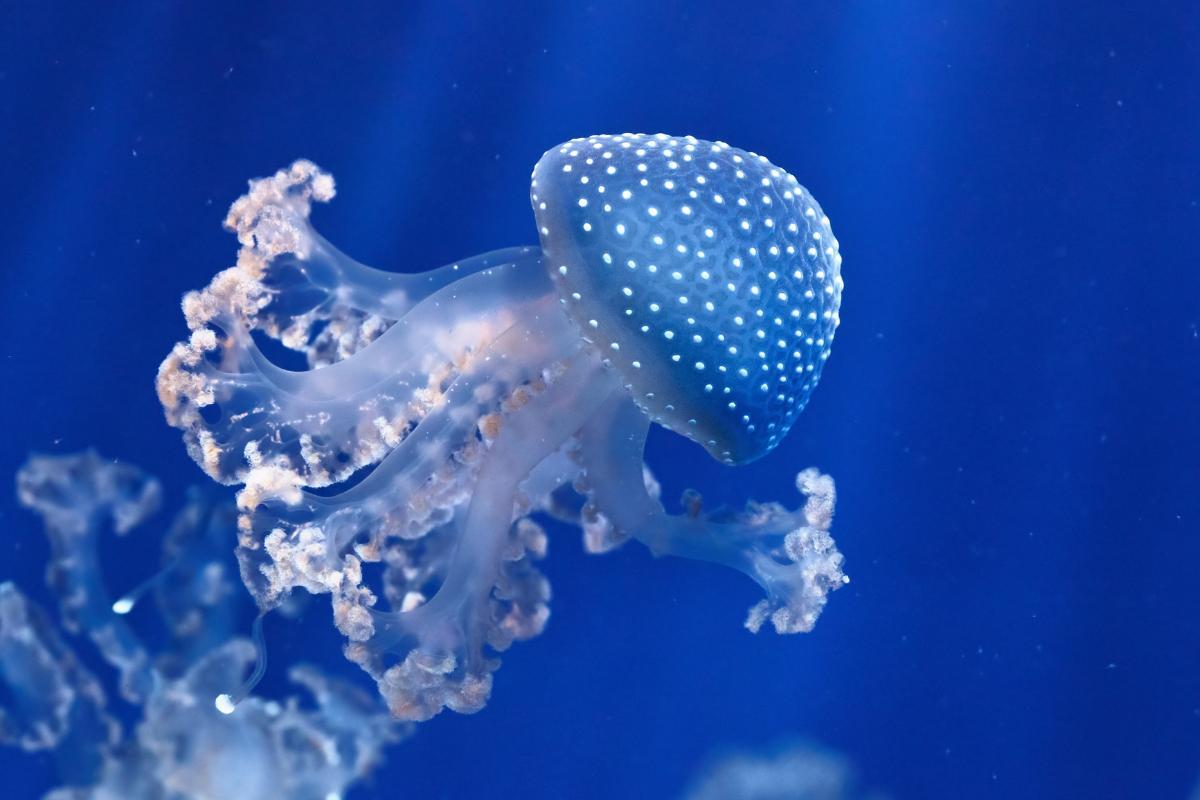
White-spotted jellyfish
Also known as the Australian spotted jellyfish or the floating bell, the white-spotted jellyfish (Phyllorhiza punctata) is a species native to the Pacific Ocean that ranges from Australia to Japan. It has been introduced and become an invasive species in other parts of the world.
The white-spotted jellyfish can reach up to 50 cm in diameter, but specimens exceeding 70 cm have been found. One of its characteristic features is that it has white spots distributed evenly across its umbrella. Like the other non-stinging jellyfish mentioned above, their venom is low in toxicity and their sting is not very irritating. They are not considered a threat to humans.
Here you can learn about all the types of Mediterranean Jellyfish.

Discomedusa lobata
Discomedusa lobata doesn't have a widely-recognized common name, but it is a species of jellyfish found mainly in the coastal waters of the Atlantic. It is distinguished by its flattened and lobed umbrela, which can reach up to 15 cm in diameter. It has a color that varies from white to light brown.
It has relatively short tentacles and is equipped with nematocysts, although its stinging effect is generally mild and not very dangerous for human beings. This species is often confused with Aurelia spp. and the characteristic that allows the differentiation between them is associated with the gonads. In jellyfish from the genus Aurelia, they have a horseshoe shape while in D. lobata they occupy the entire perimeter of the umbrella.
Now you know about the types of jellyfish that do not sting or sting very mildly, you may want to learn more about all species with our article on the parts of jellyfish anatomy.

If you want to read similar articles to Types of Non-Stinging Jellyfish, we recommend you visit our Wild animals category.
- Marambio, M., Salazar, J., Ballesteros, A., & Gili, JM (2021). Dossier of the Sea of Jellyfish project.
- Marambio, M., Ballesteros, A., López-Castillo, L., Fuentes, V., & Gili, JM (2021). Identification guide for jellyfish and other gelatinous organisms.
- Ruppert, E.E., & Barnes, R.D. (1994). Invertebrate zoology. Sixth edition.