Environment
405 articles

Living organisms are complex systems made of different types of cells, but which typically begin with only one or two cells. The amount of cells required will depend on the mode of reproduction. Within these initial cells are all the genetic information required to create the new organism, acting as the...

Environmental factors are the building blocks that shape life on Earth, determining how organisms survive, adapt, and interact within their ecosystems. From the physical and chemical conditions that create habitats to the complex web of relationships between living things, these factors work together...

Frost and freeze are common weather terms, but they are often misunderstood or used interchangeably. While both involve cold temperatures, they differ in their formation, effects, and definitions. Frost refers to a thin layer of ice crystals that forms on surfaces when the temperature drops below the dew...

Sea lilies, often mistaken for plants due to their flower-like appearance, are fascinating marine animals that belong to the echinoderm family, closely related to starfish and sea urchins. With a history spanning over 490 million years, sea lilies have adapted to a variety of deep-sea habitats and developed...
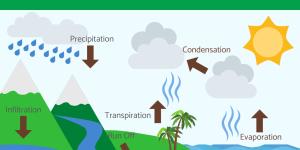
The water cycle, also known as the hydrological cycle, is one of Earth's most fundamental processes. It describes the continuous movement and transformation of water through our planet's oceans, atmosphere, and land. This natural system, which has operated for billions of years, plays a critical role...

Herbaceous plants represent a vast and diverse group in the plant kingdom, distinguished primarily by their non-woody stems and unique growth patterns. Unlike trees and shrubs, which develop woody tissue, these plants maintain soft, pliable stems throughout their life cycle. From the seasonal blooms in...

Sea sponges, scientifically known as Porifera, are among the oldest and simplest multicellular animals on Earth. These remarkable filter feeders have thrived in marine environments for over 500 million years, surviving multiple mass extinctions through their adaptable nature. From the warm waters of coral...

A storm brings some of the most intense weather you'll experience, from heavy rain to strong winds. These powerful weather events start when warm and cold air masses meet, creating a chain reaction in the atmosphere that can affect entire regions. Understanding how storms work, what types exist, and...

Water pollution poses one of the most significant environmental challenges of our time, threatening both human health and ecological systems worldwide. Every day, various contaminants enter our lakes, rivers, oceans, and groundwater, degrading these vital resources that sustain life on Earth. From industrial...

Tunicates are enthralling marine animals you've probably seen without knowing it. These filter feeders cover rocks and pier pilings along coastlines worldwide, yet most people walk right past them. At first glance, they might not look like much, but these animals tell an important story about life in the oceans...

Reducing your car's pollution doesn't require expensive upgrades or major lifestyle changes. With some simple adjustments to how you maintain and drive your vehicle, you can make a real difference in cutting emissions. From basic maintenance checks to smarter driving habits, these practical tips will...

What makes ecosystems thrive and function? Understanding the difference between biotic and abiotic factors is essential for grasping how ecosystems function. Biotic factors encompass all living organisms and their interactions, while abiotic factors comprise the non-living physical and chemical components of...

Polychaetes, commonly known as bristle worms, are some of the most intriguing creatures in marine ecosystems. With their segmented bodies, bristles, and diverse feeding habits, these worms play a vital role in ocean habitats worldwide. From burrowing lugworms to elegant fan worms, polychaetes exhibit an astonishing...

The Hadal Zone, the deepest part of the ocean, remains one of Earth’s most mysterious and unexplored regions. This dark and high-pressure environment is home to fascinating flora, resilient fauna, and a unique ecosystem that thrives against all odds. From bioluminescent creatures to microbial life surviving on...

Climate change and global warming represent two different but interconnected environmental challenges that are shaping our planet's future. While often used interchangeably, these terms describe different phenomena. Global warming refers specifically to Earth's rising average temperature, while climate...

The cytosol is an amorphous matrix that occupies the spaces between cell organelles. Its function is to act as the main site of signal transduction from the cell membrane to the nucleus and other organelles. It is often confused with the cytoplasm, a related term which encompasses all the parts of the cell...

In a world where urbanization, agriculture, and infrastructure development continue to encroach upon natural habitats, wildlife corridors have emerged as a critical strategy for conservation. These pathways, which connect fragmented ecosystems, play a vital role in ensuring the survival of countless species...

Sand dunes are accumulations of sand formed by the action of the wind. Their formation is associated with the transport of grains of sand which are deposited in large amounts when they encounter certain obstacles. There are different types of dunes, often defined by their shape and direction in which they...

Frost occurs when water vapor comes in contact with a surface that is freezing and turns to ice. While it is a meteorological phenomenon, it is not exclusively so. Frost can appear on a very cold drink or a popsicle out of the ice box. It can even appear on our nose if the conditions are conducive to...

When checking the weather, you’ve likely seen terms like "drizzle" and "rain" used to describe precipitation. But what exactly is the difference between drizzle and rain? Understanding the distinction can help you prepare for the day ahead, as these terms indicate not only varying intensities but also different...

In the world of biology, organisms are often classified based on how they obtain energy and nutrients. One such classification centers around heterotrophic organisms, which are unable to produce their own food. From the tiniest bacteria to complex animals, heterotrophs rely on external sources to fuel...

Bacterial pili are crucial, hair-like structures that extend from the surface of many bacteria, playing essential roles in survival and adaptation. These tiny appendages help bacteria adhere to surfaces, communicate with other cells, and exchange genetic material, which often leads to increased antibiotic resistance....

Rotifers are tiny animals from the phylum Rotifera, mostly microscopic organisms which inhabit freshwater aquatic environments. Sometimes known as wheel animals or wheel animalcules, they have a segmented body which is divided into a head, trunk and foot. They also have a characteristic corona which is...

The environment encompasses all the living and non-living things around us, forming the natural world that supports life on Earth. It includes everything from the air we breathe and the water we drink to the forests, oceans, and countless ecosystems that maintain the planet's balance. Each part of the...
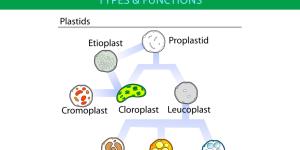
Plastids are organelles found in certain cells which play a crucial role in the survival of the organism. They are most associated with plants, but they can also be found in algae and some other eukaryotes. One of the key characteristics of plastids is that they are bound by a membrane, allowing for various...

The jet stream is a high-altitude, fast-moving ribbon of air that encircles the Earth, influencing weather patterns and climate across continents. It steers storms, shifts temperatures, and creates distinct weather zones. Formed by temperature differences between the polar and tropical regions, the jet stream...

Also known as a udometer, hyetometer or, most commonly, a rain gauge, a pluviometer is used to measure the amount of liquid precipitation which falls in a specific location during a given period. This liquid precipitation is mostly in the form of rain. knowing rainfall measurements is of great importance...

An anemometer is an instrument used to measure wind speed. This device is essential in various fields such as meteorology, aviation, energy production, navigation and even certain outdoor sports. Its operation varies depending on the type, but all models collect key information to analyze wind intensity....

An altimeter is a device that measures altitude, meaning the vertical distance between a given point and certain fixed level. In most practical uses, this fixed level is sea level. Its use is essential in various activities such as aviation, mountaineering and outdoor sports. In these capacities, accurate...

Also known as soil contamination or land pollution, soil pollution is a type of environmental degradation which affects the natural substrate of the Earth. This degradation is the result of chemical substances being released which harm the land to varying degrees, endangering ecosystems and human health...

Amyloplasts are specific plastids present in plant cells, specifically they are organelles responsible for functions such as starch synthesis and storage. Amyloplast organelles have a double membrane, composed of a smooth outer membrane and an inner membrane that invaginates to form tubules. The inner...

Porpoises are marine mammals of the Phocoenidae family. Although very similar in appearance to dolphins, they are genetically different and are more closely related to other cetaceans. Most live in ocean habitats, but there are some which are known to live in brackish waters and one which is known to...

Thunderstorms are one of nature’s most powerful and dramatic weather phenomena, often marked by flashes of lightning, rumbling thunder, and heavy rain. But have you ever wondered what causes these intense storms to form? Understanding the science behind thunderstorms can help us better appreciate their...

Industrial wastewater, a byproduct of various manufacturing processes, poses a significant threat to our environment if not properly treated. Containing harmful pollutants such as chemicals, heavy metals, and other toxic substances, this wastewater is generated by a wide range of industries, from factories...

Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) refer to the combined content of all inorganic and organic substances, including minerals, salts, metals, and other compounds, dissolved in a liquid—usually water. These particles are so small that they pass through a typical water filter, distinguishing them from suspended solids...

A barometer is an instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure, a fundamental metric for predicting changes in the weather. While they may be less common in homes than they once were, barometers are still vital pieces of equipment to help assess atmospheric conditions. In this article from thedailyECO,...

Ctenophores, commonly known as comb jellies, are marine invertebrates that, despite their jelly-like appearance, they are distinct from jellyfish. They belong to their own unique phylum, Ctenophora. Characterized by rows of cilia, or comb-like structures, these creatures use these for movement, creating a...

Climate change is a major factor contributing to the increasing frequency and intensity of hurricanes globally. As the Earth's temperature rises, weather patterns are shifting, leading to significant changes in the dynamics of these powerful storms. Understanding the complex relationship between climate change...
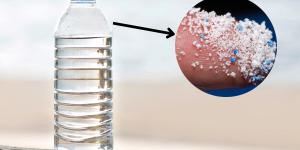
Microplastics are plastic particles that are less than 0.2" (5 mm) in size which can come from different sources. Regardless of their origins, their presence in the world's water has been exponentially increasing. Since they are found in water, they can even enter human tissue if they are sufficiently...

The various types of global climates are categorized by different factors and systems. These can be dependent on their ecosystem type, location, altitude and other determinants. The continental climate is a category of climate which is determined by the Köppen climate classification. This is a system based...

A mountain climate is the localized climate of a mountainous area. Due to the greater altitude, the atmospheric conditions are altered, resulting in lower temperatures and significant climate variability. Temperature and precipitation patterns change significantly at different altitudes. For this reason,...

The Last Universal Common Ancestor, or LUCA, represents the most recent shared ancestor of all life on Earth. LUCA is not a single organism but rather a hypothetical entity from which all modern organisms—bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes—descend. Understanding LUCA provides crucial insights into the...

Cirrocumulus are a type of cloud that forms at high altitudes, generally more than 6,000 meters above sea level. They are composed of small ice crystals. They are characterized by their appearance in groups of small white clouds that are organized in regular patterns, often being compared to fish scales....

Atmospheric pressure, the force exerted by the weight of the air above us, plays a crucial role in weather patterns, aviation, and even our daily lives. Measuring this pressure helps scientists and meteorologists predict weather changes and understand atmospheric behavior. But how exactly is atmospheric...

The Earth's atmosphere is in constant motion, driven by the uneven heating of the planet's surface by the sun. This dynamic movement, known as general atmospheric circulation, shapes global wind patterns, influences climate zones, and affects weather systems around the world. Understanding these circulation...

Also known as flooded forests, freshwater swamp forests are characterized by periodic flood by bodies of water such as rivers or lakes. While this flooding can be seasonal, it can be more frequent in certain areas. Their duration and the depth of the flooding can also vary according to region and the...

Stomata are tiny, but vital structures found on the surfaces of plant leaves and stems, playing a crucial role in the processes of gas exchange and transpiration. These microscopic pores allow plants to absorb carbon dioxide for photosynthesis while releasing oxygen and water vapor. However, not all stomata...

Chromoplasts are a type of cell organelle that are present exclusively in certain plants, algae and other eukaryotes. Specifically, they are a type of plastid. They are responsible for pigment generation in plants, meaning they give color to flowers and other parts. In addition, their functions include...

Also known as tropical dry forests, dry forests are a relative description. While rainforests have periods throughout the year when there is more rainfall, high rainfall occurs throughout the year. In a dry forest, there are distinct wet and dry seasons with periods of little to no rain. As with rainforests,...

World Car Free Day is celebrated on the 22nd September as part of a global movement that promotes sustainable mobility and the reduction of the use of private cars. This day aims to reduce the environmental impact produced by these means of transport. In turn, the hops is not only to improve people's...
