Difference Between Vascular Vs. Non-Vascular Plants


Although very different, plants are living beings which have some basic functions which are the same as animals. They need to take carry out cellular respiration and reproduce to maintain their species, as well as many other biological processes. Energy is particularly important because they would not be able to do anything without it. We may not think of plants as feeding in the same way as animals have a diet, but they have the same basic function. Plants need to derive this energy from nutrients, but they also need to transport these nutrients around their organism. It is this transportation of vital substances which informs thedailyECO as we look at the difference between vascular and non-vascular plants.
What are vascular plants?
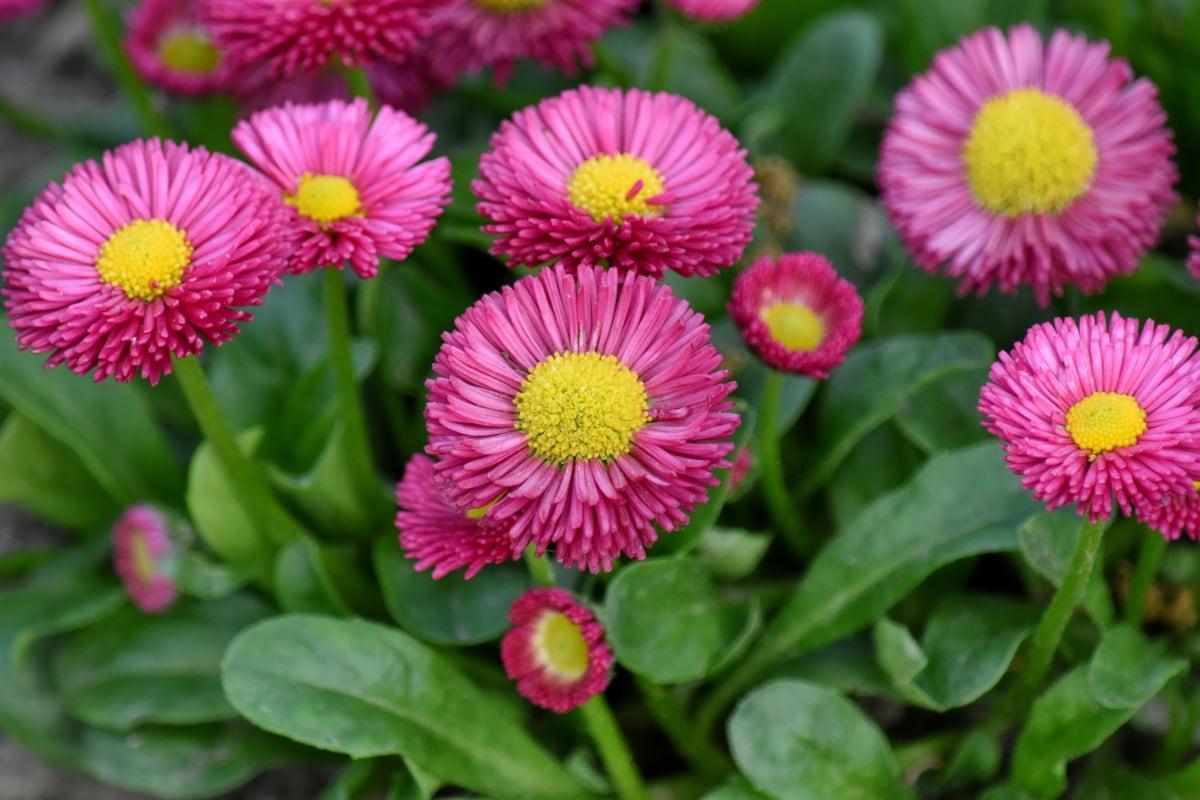
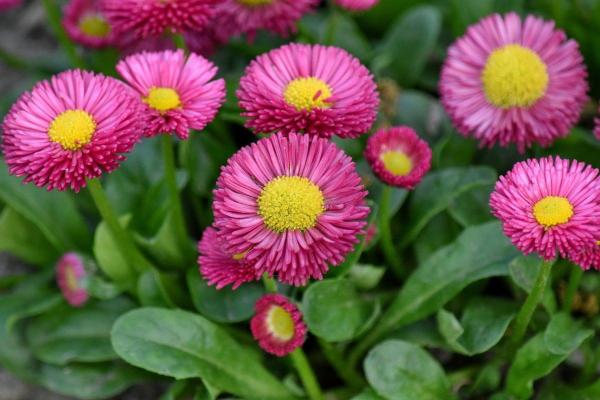
Scientifically known as tracheophytes, vascular plants are plants which have conductive and structural tissues designed to provide them with the support and energy they need for development. They have evolved these structures to achieve optimal growth. It is for this reason they are often known as higher plants, referring to a more advanced evolution.
Vascular plants are so-called due to the presence of vascular tissue. These are represented by the xylem and phloem which are both used for transportation:
- Xylem: used to transport water and minerals.
- Phloem: used to transport sugars and other nutrients.
In the vast majority of cases, vascular plants have distinct parts. Plant anatomy can include the roots, stem, leaves, flowers and fruits. These are the plants we often keep at home or the ones which are most commonly used in agriculture to cultivate as crops.
Ferns are a division of tracheophyte that are known as Polypodiopsida. They are non-flowering vascular plants which are some of the first plant groups to populate the planet. Since they do not produce flowers, they have to reproduce via spores using the process of sporulation. These unique plants always require very humid climates to grow and reproduce, but their durability makes them very popular houseplants.
Other vascular plants are flowering and have more complicated structures. These are known as angiosperms. These flowers are used to help sexually reproducing plants fertilize, protect seeds and even help with seed dispersal. An example is when flowers turn into fruit and become tasty food for certain animals who then spread the seeds after consumption.
Some gymnosperm plants are vascular. Gymnosperms do not produce true flowers, therefore they cannot turn into fruit. Their seeds are left unprotected in various structures. A common example is the pine cone which is not a type of fruit. Generally speaking, vascular plants are larger and more complex organisms that non-vascular plants. They have more complex organs and live in a wide range of habitats.
Learn more about the difference between angiosperms and gymnosperms with our related article.

What are non-vascular plants?
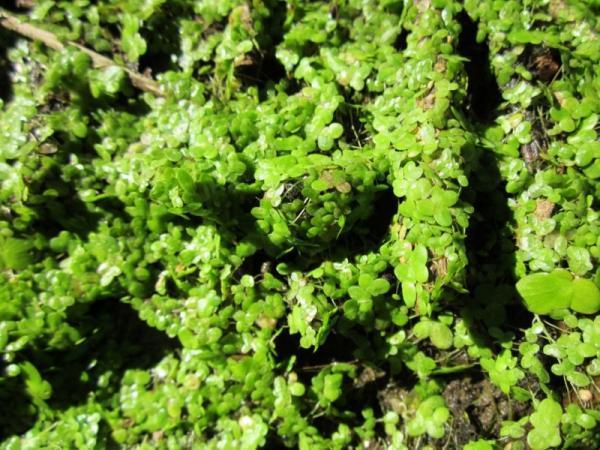
Also known as bryophytes, non-vascular plants are characterized by lacking a vascular system. Specifically, they don't have a xylem and phloem for transportation. Naturally, this may lead you to wonder how non-vascular plants are able to transport nutrients.
Bryophytes have a much more simple organism structure than tracheophytes, meaning they lack roots, stems, leaves and flowers. Non-vascular plants rely on diffusion and osmosis to move water through their organism. This water also contains dissolved substances such as sugars and other nutrients. They transport these substances across short distances from cell to cell. Many absorb moisture directly from the surrounding environment through their surfaces, aided by their thin tissues and constant exposure to humid conditions.
Due to their relatively small size, non-vascular plants are much more difficult to study than other botanical groups. This doesn't mean they are uncommon. They actually are present in almost all terrestrial ecosystems in the world, from desert areas to mountain ranges. Non-vascular plants are divided into the following three main groups:
- Mosses: are plants characterized by anchoring themselves to the ground and supporting larger plants thanks to rhizoids, primitive structures typical of bryophytes. Mosses prefer high and humid areas to grow. Depending on the species, they can grow in both shade and sunlight. Discover a particular type of this non-vascular plant with our article asking what are club mosses?
- Hornworts: consisting of the plant division Anthocerotophyta, their common name is due to their horn-like shape. They also tend to grow in humid areas, preferably in the shade. Hornworts are less widespread than mosses. Learn more with our background article explaining what are hornwort plants?
- Liverworts: these non-vascular plants lack structures that enhance their grip on the ground. They have flattened, leaf-like bodies called thalli, but do not have upright structures characteristic of mosses. They use the surface of these thalli to absorb water and nutrients directly from their environment, meaning they do not have as much need to transport around their organism.
We provide examples of these types of non-vascular plants with our article explaining what are bryophytes?
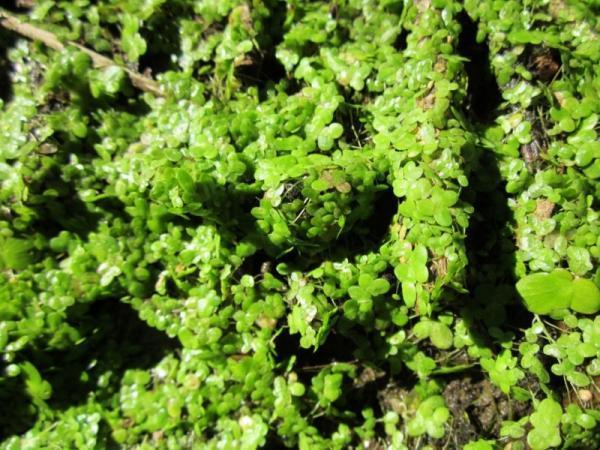

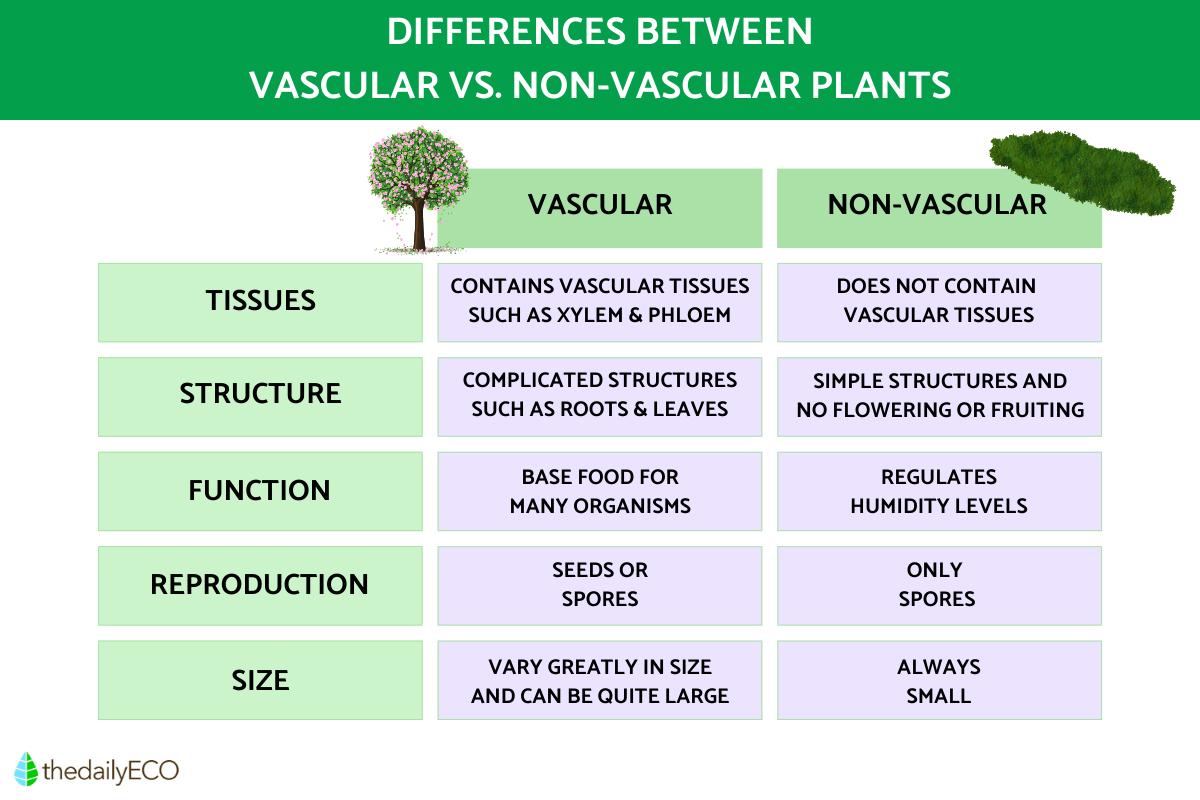
Differences between vascular vs. non-vascular plants
While we have looked at tracheophytes and bryophytes separately, here we discover the their differences by making a biological comparison:
- Structure: vascular plants have complex conductive and structural tissues that provide the plant with a foundation for optimal growth. Non-vascular plants absorb water directly from the atmosphere and lack these tissues to support growth, the reason for their relatively small size. Vascular plants do not have vascular tissue, meaning they lack a xylem and phloem for nutrient transportation.
- Anatomy: appearance can help us easily tell the difference between vascular and non-vascular plants since the former are more complicated organism. They have parts of the plant such as stems, leaves, roots and flowers which bryophytes do not have.
- Function: one of the main functions of vascular plants is to provide the nutritional basis for most living beings. Non-vascular plants are primarily responsible for regulating the humidity level of the environment in which they reside.
- Reproduction: vascular plants can reproduce by both seeds and spores, but non-vascular plants can only reproduce by spores under favorable conditions.
- Size: non-vascular plants do not usually stand out among other species due to their small size, while vascular plants occur in nature in different shapes, colors and heights. They can even grow to over 100 meters in the case of some types of trees, something that does not occur in bryophytes.

Similarity between vascular and non-vascular plants
What vascular and non-vascular plants basically have in common is that both require sunlight to carry out the process known as photosynthesis. It is through this process which they can derive their own food. This includes mineral salts, as well as water and other elements to obtain the energy needed to grow and reproduce. These means both tracheophytes and bryophytes are autotrophs.
You can learn more about this process necessary for life on Earth with our article explaining what is photosynthesis?
If you want to read similar articles to Difference Between Vascular Vs. Non-Vascular Plants, we recommend you visit our Biology category.