Biology
Delve into Biology: explore ecosystems, uncover evolutionary secrets, and analyze the dynamics of life with engaging, research-backed content designed to enlighten.
144 articles

New
New
There is an enormous variety of plant species on our planet. They have evolved to adapt to various environments and ecosystems, some inhabiting the most inhospitable environments we can imagine. These adaptations affect various aspects of their life cycle, but some of the most vital affect reproduction....

New
New
Our world's ecosystems face many threats, with many scientists claiming that biodiversity loss is so great we are currently experiencing a mass extinction event. This is when the loss of biodiversity occurs at a very high rate and to a widespread degree. There are many causes of such biodiversity loss,...

Planet Earth is more than 4.5 billion years old. Life on Earth evolved from initial molecules which eventually became the living organisms we know today which can vary greatly in complexity. While various unknown events helped to form life, others worked to curtail it or at least change its course. Included...

A plasmid is a circular genetic molecule containing DNA that is found within certain cells. It is most commonly found in bacteria, although it has been found in eukaryotic organisms such as certain types of yeast. The main function of plasmids is to act as a vehicle for introducing foreign DNA or genes...

Adaptive radiation is a process in evolution where one original species quickly splits into many new ones, each finding its own way to live in different environments. This usually happens when creatures find themselves in new places with less competition, like on isolated islands or after a big die-off...

Considered cycles of matter, biogeochemical cycles are the natural routes of transformation by which essential elements and compounds move between living organisms, the atmosphere, the Earth's crust and water. These cycles are continuous and are necessary for the regulation of the nutrients essential for life...
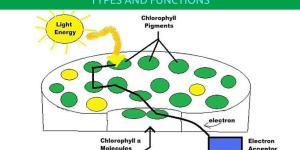
Photosynthesis is a necessary process for most life on Earth, including ourselves. Without it, ecosystems would collapse and only certain prokaryotic organisms which do not rely on it would be able to continue. Photosynthetic organisms include most plants, as well as certain types of algae and bacteria. Although...

Lysosomes are essential organelles that act as the cell’s recycling center, breaking down waste, cellular debris, and foreign invaders. These small, enzyme-filled structures play a crucial role in maintaining cell health by digesting macromolecules and recycling nutrients. Found mainly in animal cells,...

Thylakoids are membranous structures which are contained within chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They trap light energy and transduce it into the chemical energy forms known as ATP and NADPH. Thylakoids are structures where a lumen space is surrounded by a membrane. They are mainly composed of photosystems...

Lepidopterans are arthropod insects of the order Lepidoptera. They are characterized by two pairs of scaly wings, six legs, two antennae, a three-part segmented body and a modifies proboscis mouthpart. These combined characteristics apply to the insect species we know as butterflies and moths. Lepidopterans...

Making up the phylum Nemertea, nemerteans are commonly known as ribbon worms. They are unsegmented, aquatic worms that are ribbon-like in shape and inhabit shallow waters. Also known as proboscis worms, their common names refer to the presence of a long, muscular tube that can extend rapidly known as a...

Just like our bodies have different parts working together, plant roots are surprisingly complex structures. We often think of them as just anchors, but they're actually sophisticated systems with specialized tissues and regions, each essential for the plant's survival. Understanding their anatomy helps...
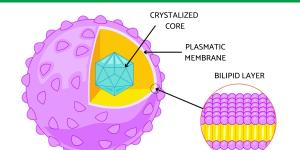
Peroxisomes are irregularly shaped cell organelles that are involved in metabolic processes and other functions within the cell. Their name originally derives from their ability to produce hydrogen peroxide as a result of lipid metabolism. Found in eukaryotes, their structure contains a lipid bilayer...

Algae are a diverse group of photosynthetic organisms that play a vital role in aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. Their global success is due in part to their impressive adaptability, which extends to their diverse reproductive strategies. From simple fragmentation to complex sexual cycles, algae...

Ethology is a branch of zoology that studies the specifics of animal behavior. By studying animal behaviors, we are able to see not only how animals interact with their environment, but how these behaviors have evolved and adapted over time. This is not only a fascinating insight into animal life, but...

Fermentation is a process where tiny organisms like bacteria and yeast cause chemical changes in food and other materials. It's how we get yogurt and wine, but it's used for much more than just food. Fermentation plays a role in everything from making energy to creating new medical materials. Different types...
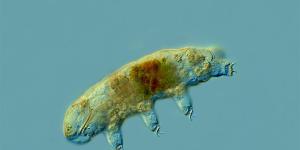
Some of the most extreme habitats in the world appear as if nothing can live in them. Whether due to high temperatures, acidity or salinity, among many other factors, life is sparse. This does not mean no life can survive in these environments. Organisms which can survive extreme conditions are known...

Archaea is a domain of unicellular microorganisms without a nucleus that are similar to bacteria. Such is their similarity that they were once considered a type of bacteria under the name archaebacteria. Domains are the highest taxonomic rank of all living organisms, with all living organisms falling under...

Living organisms are complex systems made of different types of cells, but which typically begin with only one or two cells. The amount of cells required will depend on the mode of reproduction. Within these initial cells are all the genetic information required to create the new organism, acting as the...

Herbaceous plants represent a vast and diverse group in the plant kingdom, distinguished primarily by their non-woody stems and unique growth patterns. Unlike trees and shrubs, which develop woody tissue, these plants maintain soft, pliable stems throughout their life cycle. From the seasonal blooms in...

Tunicates are enthralling marine animals you've probably seen without knowing it. These filter feeders cover rocks and pier pilings along coastlines worldwide, yet most people walk right past them. At first glance, they might not look like much, but these animals tell an important story about life in the oceans...

Polychaetes, commonly known as bristle worms, are some of the most intriguing creatures in marine ecosystems. With their segmented bodies, bristles, and diverse feeding habits, these worms play a vital role in ocean habitats worldwide. From burrowing lugworms to elegant fan worms, polychaetes exhibit an astonishing...

The cytosol is an amorphous matrix that occupies the spaces between cell organelles. Its function is to act as the main site of signal transduction from the cell membrane to the nucleus and other organelles. It is often confused with the cytoplasm, a related term which encompasses all the parts of the cell...

In the world of biology, organisms are often classified based on how they obtain energy and nutrients. One such classification centers around heterotrophic organisms, which are unable to produce their own food. From the tiniest bacteria to complex animals, heterotrophs rely on external sources to fuel...

Bacterial pili are crucial, hair-like structures that extend from the surface of many bacteria, playing essential roles in survival and adaptation. These tiny appendages help bacteria adhere to surfaces, communicate with other cells, and exchange genetic material, which often leads to increased antibiotic resistance....

Rotifers are tiny animals from the phylum Rotifera, mostly microscopic organisms which inhabit freshwater aquatic environments. Sometimes known as wheel animals or wheel animalcules, they have a segmented body which is divided into a head, trunk and foot. They also have a characteristic corona which is...
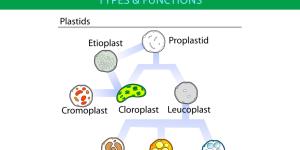
Plastids are organelles found in certain cells which play a crucial role in the survival of the organism. They are most associated with plants, but they can also be found in algae and some other eukaryotes. One of the key characteristics of plastids is that they are bound by a membrane, allowing for various...

Amyloplasts are specific plastids present in plant cells, specifically they are organelles responsible for functions such as starch synthesis and storage. Amyloplast organelles have a double membrane, composed of a smooth outer membrane and an inner membrane that invaginates to form tubules. The inner...

Porpoises are marine mammals of the Phocoenidae family. Although very similar in appearance to dolphins, they are genetically different and are more closely related to other cetaceans. Most live in ocean habitats, but there are some which are known to live in brackish waters and one which is known to...

Ctenophores, commonly known as comb jellies, are marine invertebrates that, despite their jelly-like appearance, they are distinct from jellyfish. They belong to their own unique phylum, Ctenophora. Characterized by rows of cilia, or comb-like structures, these creatures use these for movement, creating a...

The Last Universal Common Ancestor, or LUCA, represents the most recent shared ancestor of all life on Earth. LUCA is not a single organism but rather a hypothetical entity from which all modern organisms—bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes—descend. Understanding LUCA provides crucial insights into the...

Stomata are tiny, but vital structures found on the surfaces of plant leaves and stems, playing a crucial role in the processes of gas exchange and transpiration. These microscopic pores allow plants to absorb carbon dioxide for photosynthesis while releasing oxygen and water vapor. However, not all stomata...

Chromoplasts are a type of cell organelle that are present exclusively in certain plants, algae and other eukaryotes. Specifically, they are a type of plastid. They are responsible for pigment generation in plants, meaning they give color to flowers and other parts. In addition, their functions include...

Leucoplasts are small rounded structures that belong to the plastid family. These are membrane-bound organelles which are found in certain cells, mainly plants and algae. The functions of leucoplasts include lipid synthesis, carbohydrate storage and starch production. There are three types to carry out these...

Granivorous animals are those that carry out seed predation as their main form of nourishment. This means they search for seeds and grains to acquire the nutrients they need for survival. Without them, they will be unable to survive. There are other animals which will supplement their main diet with seeds,...

Clams, mussels, oysters, and scallops are just a few examples of fascinating creatures belonging to the bivalve family. These aquatic invertebrates are distinguished by their unique two-part shells, which protect their soft bodies. Whether they inhabit freshwater lakes or salty oceans, bivalves play a crucial...

Nature is a complex interplay of competition and cooperation. While survival often hinges on outcompeting others, many species have evolved mutually beneficial relationships. Unlike the predator-prey dynamic where one thrives at the expense of another, mutualism represents a win-win scenario, with both...

Life as we know it thrives within specific parameters, but Earth is also home to extraordinary organisms that defy these limitations. Among them are halophilic bacteria, microbes that not only survive but flourish in environments saturated with salt. From the depths of salt mines to the sun-baked surfaces...

Have you ever stopped to think about how some animals in the vast ocean manage to find sustenance? Unlike the known powerful predators with razor-sharp teeth, many aquatic creatures rely on a much more delicate approach – filter feeding. These fascinating animals are the ultimate opportunists, extracting...

Glial cells are structural, metabolic and trophic support cells for neurons. They are found in both the central nervous system and in the peripheral nervous system. For any function in an organism to be carried out, specialized cells are required. Despite being part of the central nervous system, glial cells...

Woody plants are a diverse and essential group of flora characterized by their durable, lignified stems and trunks. Defined by their robust internal structure, called secondary xylemthey, they differ significantly from their soft-stemmed herbaceous counterparts. These plants form the backbone of many...

Berries are more than just a tasty treat. They're a fascinating example of co-evolution, a partnership between plants and animals that benefits both sides. As animals munch on the berries, they also help spread the plant's seeds far and wide. And forget the image of berries as all small and round. They...

Also known as the horse family, equines are part of the taxonomic family Equidae. In the order Perissodactyla, they are four-legged mammals which are defined by robust bodies, placental birth, herbivorous diet and herd living. There are various types of equines, all with their own specific characteristics....

Seed dispersal is the process by which seeds are moved away from the parent plant. Plants can't walk around and sow their seeds in new locations, so they've evolved clever ways to hitch a ride on wind, water, animals, or even just rely on gravity. This movement not only increases individual plant survival...

The blueprint of life, DNA, holds the secrets of inheritance and variation. But how does this blueprint get shuffled and combined to create new possibilities? Enter genetic recombination, a fascinating process where genetic material is exchanged between chromosomes, leading to a vibrant dance of genes....

As part of the larger cell nucleus, the nucleolus is a suborganelle which is responsible for the biosynthesis of ribosomes in the cell, among other functions. It is a nuclear body which is distinguished by its presence as a dark, spherical structure within the nucleus of cells. Its own structure that...

Binary fission is a method of asexual reproduction that involves the simultaneous duplication of DNA and division of the cytoplasm. In doing so, it generates two identical daughter cells. This mainly takes place in prokaryotic cells such as bacteria, but it can also take place in unicellular eukaryotes....

Ever admired a rose up close and then compared it to a tulip? Unlike most flowers, the colorful parts of a tulip aren't classic petals, but rather structures called tepals. While petals are the usual colorful attractors for pollinators, some flowers, like tulips or lilies, have these unique tepals....

Chromatophores are specialized cells that contain internal pigments that reflect light. The functions of chromatophores include camouflage, communication and protection against ultraviolet radiation. There are different types of chromatophores, including melanophores, erythrophores, xanthophores, iridophores...

The nucleoid is a characteristic feature of prokaryotic cells, houses the organism's genetic material and plays pivotal roles in genetic storage, DNA replication, transcription, and gene regulation. It is formed through the condensation and functional organization of a single chromosomal DNA molecule.
In...
